Nucleoside-modified mRNA encoding HSV-2 glycoproteins C, D, and E prevents clinical and subclinical genital herpes
- PMID: 31541030
- PMCID: PMC6822172
- DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aaw7083
Nucleoside-modified mRNA encoding HSV-2 glycoproteins C, D, and E prevents clinical and subclinical genital herpes
Abstract
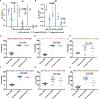
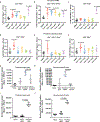
The goals of a genital herpes vaccine are to prevent painful genital lesions and reduce or eliminate subclinical infection that risks transmission to partners and newborns. We evaluated a trivalent glycoprotein vaccine containing herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) entry molecule glycoprotein D (gD2) and two immune evasion molecules: glycoprotein C (gC2), which binds complement C3b, and glycoprotein E (gE2), which blocks immunoglobulin G (IgG) Fc activities. The trivalent vaccine was administered as baculovirus proteins with CpG and alum, or the identical amino acids were expressed using nucleoside-modified mRNA in lipid nanoparticles (LNPs). Both formulations completely prevented genital lesions in mice and guinea pigs. Differences emerged when evaluating subclinical infection. The trivalent protein vaccine prevented dorsal root ganglia infection, and day 2 and 4 vaginal cultures were negative in 23 of 30 (73%) mice compared with 63 of 64 (98%) in the mRNA group (P = 0.0012). In guinea pigs, 5 of 10 (50%) animals in the trivalent subunit protein group had vaginal shedding of HSV-2 DNA on 19 of 210 (9%) days compared with 2 of 10 (20%) animals in the mRNA group that shed HSV-2 DNA on 5 of 210 (2%) days (P = 0.0052). The trivalent mRNA vaccine was superior to trivalent proteins in stimulating ELISA IgG antibodies, neutralizing antibodies, antibodies that bind to crucial gD2 epitopes involved in entry and cell-to-cell spread, CD4+ T cell responses, and T follicular helper and germinal center B cell responses. The trivalent nucleoside-modified mRNA-LNP vaccine is a promising candidate for human trials.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures




References
-
- Brown ZA, Selke S, Zeh J, Kopelman J, Maslow A, Ashley RL, Watts DH, Berry S, Herd M, Corey L, The acquisition of herpes simplex virus during pregnancy. N Engl J Med 337, 509–515 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Kimberlin DW, Lin CY, Jacobs RF, Powell DA, Corey L, Gruber WC, Rathore M, Bradley JS, Diaz PS, Kumar M, Arvin AM, Gutierrez K, Shelton M, Weiner LB, Sleasman JW, de Sierra TM, Weller S, Soong SJ, Kiell J, Lakeman FD, Whitley RJ, Safety and efficacy of high-dose intravenous acyclovir in the management of neonatal herpes simplex virus infections. Pediatrics 108, 230–238 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Poole CL, Kimberlin DW, Antiviral Approaches for the Treatment of Herpes Simplex Virus Infections in Newborn Infants. Annu Rev Virol 5, 407–425 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

