Externalizing Behaviors Buffer the Effects of Early Life Adversity on Physiologic Dysregulation
- PMID: 31541131
- PMCID: PMC6754506
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-49461-x
Externalizing Behaviors Buffer the Effects of Early Life Adversity on Physiologic Dysregulation
Abstract
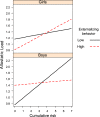
The present study examined the counterintuitive hypothesis that externalizing behaviors such as aggression, although in many respects detrimental, may be functional and protect against the detrimental health consequences of early life adversity. In particular, in line with evolutionary models of development, we argue that externalizing problems moderate the association between chronic stress exposure and allostatic load, a biological marker of chronic physiological dysregulation. Prospective interactive effects of externalizing behaviors and cumulative risk (a confluence of multiple risk factors) on children's allostatic load were assessed in 260 children (46% female, baseline age = 9). Exposure to early life adversity was assessed at baseline using a cumulative risk index. Externalizing behaviors were reported by parents at baseline. Allostatic load was measured at baseline and at ages 13 and 17, using endocrine, cardiovascular and metabolic parameters. Results of linear-mixed effects models indicated that the association between cumulative risk and allostatic load was attenuated for adolescents who scored high on externalizing behaviors. Further examination of sex differences indicated that the findings were more pronounced among males than females.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In risky environments, emotional children have more behavioral problems but lower allostatic load.Health Psychol. 2017 May;36(5):468-476. doi: 10.1037/hea0000459. Epub 2017 Feb 9. Health Psychol. 2017. PMID: 28182450
-
Linking childhood allostatic load, early adversity and the emergence of mental health symptoms in early adulthood: Analysis of the ALSPAC longitudinal birth cohort.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2025 Feb;172:107276. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2024.107276. Epub 2024 Dec 31. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2025. PMID: 39787866
-
The mediating role of allostatic load in the relationship between early life adversity and cognitive function across the adult lifespan.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2022 Jul;141:105761. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2022.105761. Epub 2022 Apr 6. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2022. PMID: 35429700
-
Allostasis and allostatic load: expanding the discourse on stress and cardiovascular disease.J Clin Nurs. 2008 Apr;17(7B):201-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2702.2008.02347.x. J Clin Nurs. 2008. PMID: 18578796 Review.
-
The cost of chronic stress in childhood: understanding and applying the concept of allostatic load.Psychodyn Psychiatry. 2012 Sep;40(3):469-80. doi: 10.1521/pdps.2012.40.3.469. Psychodyn Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 23002705 Review.
Cited by
-
Relations between adolescent perceptions of household chaos and externalizing and internalizing behaviors in low- and middle-income families.J Res Adolesc. 2024 Dec;34(4):1500-1516. doi: 10.1111/jora.13016. Epub 2024 Aug 29. J Res Adolesc. 2024. PMID: 39210556 Free PMC article.
-
Does Executive Functioning Moderate the Association Between Psychopathic Traits and Antisocial Behavior in Youth?Res Child Adolesc Psychopathol. 2025 Apr;53(4):543-554. doi: 10.1007/s10802-024-01283-w. Epub 2025 Jan 25. Res Child Adolesc Psychopathol. 2025. PMID: 39869283 Free PMC article.
-
Resilience and Family Socialization Processes in Ethnic Minority Youth: Illuminating the Achievement-Health Paradox.Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev. 2022 Mar;25(1):75-92. doi: 10.1007/s10567-022-00389-1. Epub 2022 Feb 24. Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev. 2022. PMID: 35201542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Allostatic Load in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review.Psychother Psychosom. 2023;92(5):295-303. doi: 10.1159/000533424. Epub 2023 Sep 4. Psychother Psychosom. 2023. PMID: 37666236 Free PMC article.
-
Early life stress and substance use disorders: The critical role of adolescent substance use.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2022 Apr;215:173360. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2022.173360. Epub 2022 Feb 25. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2022. PMID: 35219756 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Huaqing Qi C, Kaiser AP. Behavior Problems of Preschool Children From Low-Income Families: Review of the Literature. Top. Early Child. Spec. Educ. 2003;23:188–216. doi: 10.1177/02711214030230040201. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases