The efficacy and safety of botulinum toxin type A in treatment of trigeminal neuralgia and peripheral neuropathic pain: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 31541518
- PMCID: PMC6790324
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.1409
The efficacy and safety of botulinum toxin type A in treatment of trigeminal neuralgia and peripheral neuropathic pain: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background: Although recent studies have shown that botulinum toxin-A (BTX-A) has a good analgesic effect on trigeminal neuralgia (TN) and peripheral neuropathic pain (PNP), the quality of evidence is low due to limited data. This meta-analysis is used to synthesize existing evidence for the treatment of these conditions with BTX-A.
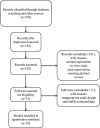
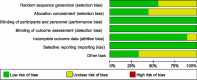
Methods: Relevant trials were accessed by using an electronic search in databases (Web of Science, PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, and ClinicalTrials.gov). Data from included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) on the efficacy and safety of BTX-A in treating TN and PNP were extracted for meta-analysis.
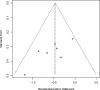
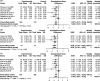
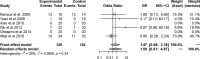
Results: Finally, 10 RCTs (n = 391) were included in this meta-analysis. The pooled effect of BTX-A was superior to placebo based on pain intensity (SMD = -0.48, 95% CI [-0.74, 0.23] at 1 month, SMD = -0.58, 95% CI [-0.91, -0.24] at 2 months, and SMD = -0.55, 95% CI [-0.87, -0.22] at 3 months). Number needed to treat (NNT) for 50% pain intensity reduction showed better effect of BTX-A on TN and postherpetic neuralgia (PN). Adverse events associated with BTX-A were similar to placebo (OR = 1.58, 95% CI [0.51, 4.87], p = .424).
Conclusion: Pooled data from our meta-analysis suggest that BTX-A is efficacious and safe in treating TN and PNP. However, due to the limited sample size and heterogeneity, further larger and well-designed RCTs are imperative to validate these findings.
Keywords: botulinum toxin-A; meta-analysis; peripheral neuropathic pain; randomized controlled trials; trigeminal neuralgia.
© 2019 The Authors. Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Attal, N. , de Andrade, D. C. , Adam, F. , Ranoux, D. , Teixeira, M. J. , Galhardoni, R. , … Bouhassira, D. (2016). Safety and efficacy of repeated injections of botulinum toxin A in peripheral neuropathic pain (BOTNEP): A randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. The Lancet Neurology, 15(6), 555–565. 10.1016/s1474-4422(16)00017-x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

