Alcohol use disorder and cannabis use disorder symptomatology in adolescents are differentially related to dysfunction in brain regions supporting face processing
- PMID: 31541926
- PMCID: PMC6992382
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2019.09.004
Alcohol use disorder and cannabis use disorder symptomatology in adolescents are differentially related to dysfunction in brain regions supporting face processing
Abstract
Despite extensive behavioral evidence of impairments in face processing and expression recognition in adults with alcohol or cannabis use disorders (AUD/CUD), neuroimaging findings have been inconsistent. Moreover, relatively little work has examined the relationship of AUD or CUD symptoms with face or expression processing within adolescents. Given the high prevalence of alcohol and cannabis use during adolescence, understanding how these usage behaviors interact with neural mechanisms supporting face and expression processing could have important implications for youth social and emotional functioning. In this study, adolescents (N = 104) responded to morphed fearful and happy expressions during fMRI and their level of AUD and/or CUD symptoms were related to the BOLD response data. We found that AUD and CUD symptom severity were both negatively related to responses to faces generally. However, whereas this relationship was shown for AUD within ventromedial prefrontal cortex and lingual gyrus, it was shown for CUD within rostromedial prefrontal cortex including anterior cingulate cortex. Additionally, AUD symptom levels were associated with differential responses within medial temporal pole and inferior parietal lobule as a function of expression. These results have potential implications for understanding the social and emotional functioning of adolescents with AUD and CUD symptoms.
Keywords: Adolescence; Alcohol; Cannabis; Expressions; Faces; fMRI.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
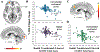

References
-
- Achenbach TM, Rescorla LA, 2001. Manual for the ASEBA school-age forms & profiles: An integrated system of multi-informant assessment. Burlington, VT: Unviersity of Vermont, Research Center for Children, Youth, & Families.
-
- Aloi J, Blair KS, Crum KI, Meffert H, White SF, Tyler PM, Thornton LC, Mobley AM, Killanin AD, Adams KO, Filbey F, Pope K, Blair RJR, 2018. Adolescents show differential dysfunctions related to Alcohol and Cannabis Use Disorder severity in emotion and executive attention neuro-circuitries. Neuroimage Clin. 19, 782–792. 10.1016/j.nicl.2018.06.005 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Angold A, Costello EJ, Messer SC, Pickles A, Winder F, Silver D, 1995. The development of a short questionnaire for use in epidemiological studies of depression in children and adolescents. Int. J. Methods Psychiatr. Res 5, 237–249.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

