Mechanisms of IFNalpha-1a-Induced Apoptosis in a Laryngeal Cancer Cell Line
- PMID: 31542790
- PMCID: PMC6774267
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.917097
Mechanisms of IFNalpha-1a-Induced Apoptosis in a Laryngeal Cancer Cell Line
Abstract
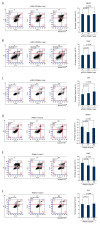
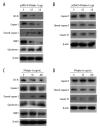
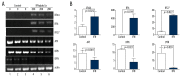
BACKGROUND Interferon alpha (IFNalpha) exerts its anti-proliferative effect on many human cancers. Among the 13 subtypes of human IFNalpha, IFNalpha-1 subtype has 2 variants, named IFNalpha-1a and IFNalpha-1b, that differ from each other in only 1 amino acid, at residue 114. However, the mechanism by which IFNalpha-1a mediates growth inhibition is still unclear. MATERIAL AND METHODS Human laryngeal carcinoma HEp2 cells were treated with IFNalpha-1a by either transient transfection or exogenous delivery. Western blot and RT-PCR analysis were carried out to assess apoptotic pathways active in IFNalpha-1a-treated HEp2 cells. Microarray analysis was conducted to uncover the differential gene expressions after IFNalpha-1a treatment. KEGG pathway enrichment analysis was also performed. RESULTS IFNalpha-1a markedly inhibited the proliferation and significantly promoted the apoptosis of HEp-2 cells. Mechanistic studies indicate that IFNalpha-1a-mediated cell apoptosis is directly linked to intrinsic and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-related apoptosis, but is independent of extrinsic apoptosis. The top 40 differentially expressed genes discovered by microarray analysis included 20 upregulated genes (e.g., IFI6, IFI27, IFI44L, and MIR548X) and 20 downregulated genes (e.g., PRKDC, HIST1H3B, DYNC1H1, and HIST1H2AM). KEGG pathway enrichment analysis revealed that 4 out of 6 pathways are TP53-related. CONCLUSIONS We demonstrated a detailed mechanism involved in IFNalpha-1a-mediated anti-proliferation activity in human laryngeal carcinoma cells.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures




References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Kuper H, Boffetta P, Adami HO. Tobacco use and cancer causation: Association by tumour type. J Intern Med. 2002;252:206–24. - PubMed
-
- Boffetta P, Hashibe M. Alcohol and cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2006;7:149–56. - PubMed
-
- Sanchez Barrueco A, Gonzalez Galan F, Lora Pablos D, et al. HPV in larynx squamous cell carcinoma: New serotypes and survival study within 10-year follow-up. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017;156:677–82. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

