High-Intensity Interval Training in Cardiac Rehabilitation
- PMID: 31543179
- PMCID: PMC6760312
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cger.2019.07.011
High-Intensity Interval Training in Cardiac Rehabilitation
Abstract
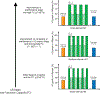
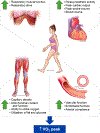
Recently, high-intensity interval training (HIIT) has been recognized as a safe and effective alternative to moderate-intensity continuous training for older patients with cardiovascular disease (CVD) in cardiac rehabilitation settings in an effort to improve health outcomes. This brief review considers general principles and suggestions for prescription of HIIT for older patients with CVD, specific challenges pertaining to older adults, the physiologic mechanisms by which HIIT contributes to improvements in peak Vo2, and the effects of HIIT on cardiovascular health in older patients with coronary artery disease and heart failure.
Keywords: Cardiac rehabilitation; Cardiovascular disease; Exercise prescription; Frailty; Interval training; Old age; Peak oxygen uptake.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Schopfer DW, Forman DE. Cardiac Rehabilitation in Older Adults. Can J Cardiol 2016;32(9):1088–1096. - PubMed
-
- Myers J, Prakash M, Froelicher V, Do D, Partington S, Atwood JE. Exercise capacity and mortality among men referred for exercise testing. N Engl J Med 2002;346(11):793–801. - PubMed
-
- Piepoli MF, Hoes AW, Agewall S, et al. 2016 European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice: The Sixth Joint Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and Other Societies on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice (constituted by representatives of 10 societies and by invited experts)Developed with the special contribution of the European Association for Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation (EACPR). Eur Heart J 2016;37(29):2315–2381. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Keteyian SJ, Hibner BA, Bronsteen K, et al. Greater improvement in cardiorespiratory fitness using higher-intensity interval training in the standard cardiac rehabilitation setting. J Cardiopulm Rehabil Prev 2014;34(2):98–105. - PubMed
-
- Conraads VM, Pattyn N, De Maeyer C, et al. Aerobic interval training and continuous training equally improve aerobic exercise capacity in patients with coronary artery disease: the SAINTEX-CAD study. Int J Cardiol 2015;179(1):203–210. - PubMed

