Organization of Chromatin by Intrinsic and Regulated Phase Separation
- PMID: 31543265
- PMCID: PMC6778041
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.08.037
Organization of Chromatin by Intrinsic and Regulated Phase Separation
Abstract
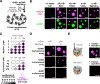
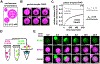
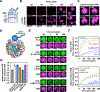
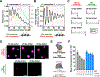
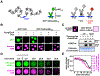
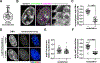
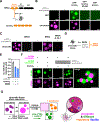
Eukaryotic chromatin is highly condensed but dynamically accessible to regulation and organized into subdomains. We demonstrate that reconstituted chromatin undergoes histone tail-driven liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) in physiologic salt and when microinjected into cell nuclei, producing dense and dynamic droplets. Linker histone H1 and internucleosome linker lengths shared across eukaryotes promote phase separation of chromatin, tune droplet properties, and coordinate to form condensates of consistent density in manners that parallel chromatin behavior in cells. Histone acetylation by p300 antagonizes chromatin phase separation, dissolving droplets in vitro and decreasing droplet formation in nuclei. In the presence of multi-bromodomain proteins, such as BRD4, highly acetylated chromatin forms a new phase-separated state with droplets of distinct physical properties, which can be immiscible with unmodified chromatin droplets, mimicking nuclear chromatin subdomains. Our data suggest a framework, based on intrinsic phase separation of the chromatin polymer, for understanding the organization and regulation of eukaryotic genomes.
Keywords: BRD4; acetylation; chromatin organization; epigenetics; genome; histone; histone H1; nucleosome; nucleosome spacing; phase separation.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
M.K.R. is a consultant with Third Rock Ventures.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

