Loss of SATB1 Induces p21-Dependent Cellular Senescence in Post-mitotic Dopaminergic Neurons
- PMID: 31543366
- PMCID: PMC7493192
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2019.08.013
Loss of SATB1 Induces p21-Dependent Cellular Senescence in Post-mitotic Dopaminergic Neurons
Abstract
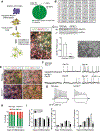
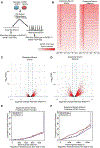
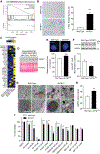
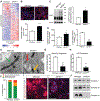
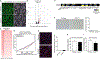
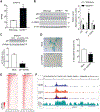
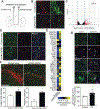
Cellular senescence is a mechanism used by mitotic cells to prevent uncontrolled cell division. As senescent cells persist in tissues, they cause local inflammation and are harmful to surrounding cells, contributing to aging. Generally, neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson's, are disorders of aging. The contribution of cellular senescence to neurodegeneration is still unclear. SATB1 is a DNA binding protein associated with Parkinson's disease. We report that SATB1 prevents cellular senescence in post-mitotic dopaminergic neurons. Loss of SATB1 causes activation of a cellular senescence transcriptional program in dopamine neurons both in human stem cell-derived dopaminergic neurons and in mice. We observed phenotypes that are central to cellular senescence in SATB1 knockout dopamine neurons in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, we found that SATB1 directly represses expression of the pro-senescence factor p21 in dopaminergic neurons. Our data implicate senescence of dopamine neurons as a contributing factor in the pathology of Parkinson's disease.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; SATB1; cellular senescence; dopamine; neurodegeneration; neuroinflammation; p21; senolytics; stem cells; transcriptomics.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Acosta JC, O’Loghlen A, Banito A, Guijarro MV, Augert A, Raguz S, Fumagalli M, Da Costa M, Brown C, Popov N, et al. (2008). Chemokine signaling via the CXCR2 receptor reinforces senescence. Cell 133, 1006–1018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

