The myotubularin MTMR4 regulates phagosomal phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate turnover and phagocytosis
- PMID: 31543504
- PMCID: PMC6851315
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009133
The myotubularin MTMR4 regulates phagosomal phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate turnover and phagocytosis
Abstract
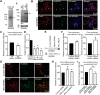
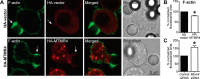
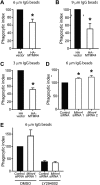
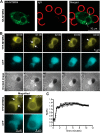
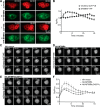
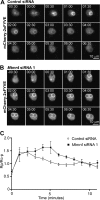
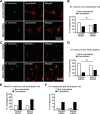
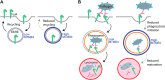
Macrophage phagocytosis is required for effective clearance of invading bacteria and other microbes. Coordinated phosphoinositide signaling is critical both for phagocytic particle engulfment and subsequent phagosomal maturation to a degradative organelle. Phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PtdIns(3)P) is a phosphoinositide that is rapidly synthesized and degraded on phagosomal membranes, where it recruits FYVE domain- and PX motif-containing proteins that promote phagosomal maturation. However, the molecular mechanisms that regulate PtdIns(3)P removal from the phagosome have remained unclear. We report here that a myotubularin PtdIns(3)P 3-phosphatase, myotubularin-related protein-4 (MTMR4), regulates macrophage phagocytosis. MTMR4 overexpression reduced and siRNA-mediated Mtmr4 silencing increased levels of cell-surface immunoglobulin receptors (i.e. Fcγ receptors (FcγRs)) on RAW 264.7 macrophages, associated with altered pseudopodal F-actin. Furthermore, MTMR4 negatively regulated the phagocytosis of IgG-opsonized particles, indicating that MTMR4 inhibits FcγR-mediated phagocytosis, and was dynamically recruited to phagosomes of macrophages during phagocytosis. MTMR4 overexpression decreased and Mtmr4-specific siRNA expression increased the duration of PtdIns(3)P on phagosomal membranes. Macrophages treated with Mtmr4-specific siRNA were more resistant to Mycobacterium marinum-induced phagosome arrest, associated with increased maturation of mycobacterial phagosomes, indicating that extended PtdIns(3)P signaling on phagosomes in the Mtmr4-knockdown cells permitted trafficking of phagosomes to acidic late endosomal and lysosomal compartments. In conclusion, our findings indicate that MTMR4 regulates PtdIns(3)P degradation in macrophages and thereby controls phagocytosis and phagosomal maturation.
Keywords: Fc-gamma receptor; innate immunity; macrophage; mycobacteria; myotubularin-related protein-4 (MTMR4); phagocytosis; phagosome; phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PtdIns(3)P); phosphatidylinositol phosphatase.
© 2019 Sheffield et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modulation of cellular phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate levels in primary macrophages affects heat-killed but not viable Mycobacterium avium's transport through the phagosome maturation process.Cell Microbiol. 2004 Oct;6(10):973-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2004.00415.x. Cell Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15339272
-
The myotubularin phosphatase MTMR4 regulates sorting from early endosomes.J Cell Sci. 2010 Sep 15;123(Pt 18):3071-83. doi: 10.1242/jcs.060103. Epub 2010 Aug 24. J Cell Sci. 2010. PMID: 20736309
-
PIKfyve inhibition interferes with phagosome and endosome maturation in macrophages.Traffic. 2014 Oct;15(10):1143-63. doi: 10.1111/tra.12199. Epub 2014 Aug 16. Traffic. 2014. PMID: 25041080
-
Protein targeting to endosomes and phagosomes via FYVE and PX domains.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2004;282:89-115. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-18805-3_4. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14594215 Review.
-
A guide to measuring phagosomal dynamics.FEBS J. 2021 Mar;288(5):1412-1433. doi: 10.1111/febs.15506. Epub 2020 Aug 16. FEBS J. 2021. PMID: 32757358 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hallmarks of aging-based dual-purpose disease and age-associated targets predicted using PandaOmics AI-powered discovery engine.Aging (Albany NY). 2022 Mar 29;14(6):2475-2506. doi: 10.18632/aging.203960. Epub 2022 Mar 29. Aging (Albany NY). 2022. PMID: 35347083 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vieira O. V., Botelho R. J., Rameh L., Brachmann S. M., Matsuo T., Davidson H. W., Schreiber A., Backer J. M., Cantley L. C., and Grinstein S. (2001) Distinct roles of class I and class III phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases in phagosome formation and maturation. J. Cell Biol. 155, 19–25 10.1083/jcb.200107069 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

