Crosstalk network among multiple inflammatory mediators in liver fibrosis
- PMID: 31543677
- PMCID: PMC6737310
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i33.4835
Crosstalk network among multiple inflammatory mediators in liver fibrosis
Abstract
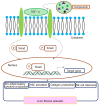
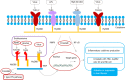
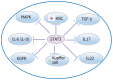
Liver fibrosis is the common pathological basis of all chronic liver diseases, and is the necessary stage for the progression of chronic liver disease to cirrhosis. As one of pathogenic factors, inflammation plays a predominant role in liver fibrosis via communication and interaction between inflammatory cells, cytokines, and the related signaling pathways. Damaged hepatocytes induce an increase in pro-inflammatory factors, thereby inducing the development of inflammation. In addition, it has been reported that inflammatory response related signaling pathway is the main signal transduction pathway for the development of liver fibrosis. The crosstalk regulatory network leads to hepatic stellate cell activation and proinflammatory cytokine production, which in turn initiate the fibrotic response. Compared with the past, the research on the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis has been greatly developed. However, the liver fibrosis mechanism is complex and many pathways involved need to be further studied. This review mainly focuses on the crosstalk regulatory network among inflammatory cells, cytokines, and the related signaling pathways in the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory liver diseases. Moreover, we also summarize the recent studies on the mechanisms underlying liver fibrosis and clinical efforts on the targeted therapies against the fibrotic response.
Keywords: Crosstalk network; Cytokine signal pathway; Inflammatory cell; Liver fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: No potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metabolic inflammation as an instigator of fibrosis during non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 May 7;26(17):1993-2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i17.1993. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32536770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FXR agonist obeticholic acid reduces hepatic inflammation and fibrosis in a rat model of toxic cirrhosis.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 16;6:33453. doi: 10.1038/srep33453. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27634375 Free PMC article.
-
LPS-induced TNF-α factor mediates pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrogenic pattern in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 8;6(39):41434-52. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5163. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26573228 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of canonical WNT signaling pathway by β-catenin/CBP inhibitor ICG-001 ameliorates liver fibrosis in vivo through suppression of stromal CXCL12.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018 Mar;1864(3):804-818. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.12.001. Epub 2017 Dec 5. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018. PMID: 29217140
-
Management strategies for liver fibrosis.Ann Hepatol. 2017 Jan-Feb;16(1):48-56. doi: 10.5604/16652681.1226814. Ann Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 28051792 Review.
Cited by
-
Animal and Organoid Models of Liver Fibrosis.Front Physiol. 2021 May 26;12:666138. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.666138. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34122138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resveratrol protects against Schistosoma mansoni-induced liver fibrosis by targeting the Sirt-1/NF-κB axis.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Feb;32(1):763-775. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01382-y. Epub 2023 Dec 2. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 38041753 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic circadian and differentiation factors control liver susceptibility for fatty liver disease and tumorigenesis.FASEB J. 2022 Sep;36(9):e22482. doi: 10.1096/fj.202101398R. FASEB J. 2022. PMID: 35947136 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficient individuals have circulating extracellular vesicles with profibrogenic cargo.Cell Commun Signal. 2020 Sep 4;18(1):140. doi: 10.1186/s12964-020-00648-0. Cell Commun Signal. 2020. PMID: 32887613 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma Kallikrein as a Modulator of Liver Injury/Remodeling.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 9;12:715111. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.715111. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34566641 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miao CG, Yang YY, He X, Huang C, Huang Y, Zhang L, Lv XW, Jin Y, Li J. Wnt signaling in liver fibrosis: progress, challenges and potential directions. Biochimie. 2013;95:2326–2335. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

