Tai Chi and whole-body vibrating therapy in sarcopenic men in advanced old age: a clinical randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 31543722
- PMCID: PMC6728405
- DOI: 10.1007/s10433-019-00498-x
Tai Chi and whole-body vibrating therapy in sarcopenic men in advanced old age: a clinical randomized controlled trial
Abstract
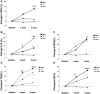
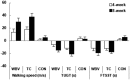
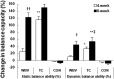
This study was to investigate the effects of Tai Chi (TC) and whole-body vibration (WBV) exercise in sarcopenic men in advanced old age. Ninety sarcopenic men (mean age 88.6 years; age range 85-101 years) were divided into three groups: TC group, WBV group, and control (CON) group. Patients in the two treatment groups received 8 weeks of training in either TC or WBV, while the control group received reminders not to change their level of physical exercise or lifestyle. Patients in all groups also received health information related to sarcopenia. Muscle mass, muscle strength, and physical performance [balance, gait speed, timed-up-and-go test (TUGT), and five-times-sit-to-stand test (FTSST)] were analyzed and compared among the three groups. Finally, seventy-nine subjects completed the study (TC n = 24; WBV n = 28; and CON 27). Muscle strength was significantly increased in the TC and WBV groups compared to the control group (P < 0.01). Following 8 weeks of exercise, improvements were observed in all physical performance tests for the TC and WBV groups (P < 0.05). The improvement in balance was greater in the TC group than the WBV group. Time × Group effects revealed significant improvements in muscle strength in the lower extremities (P < 0.05) and physical performance (P < 0.01) in both the TC and WBV groups. Changes in muscle mass, as measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, did not significantly differ between groups. These findings indicate that TC and WBV are effective treatments for improving muscle strength and physical performance in sarcopenic men in advanced old age.
Keywords: Advanced old age; Sarcopenia; Tai Chi; Whole-body vibration.
Figures
References
-
- Bogaerts A, Delecluse C, Claessens AL, Coudyzer W, Boonen S, Ver-schueren SM. Impact of whole-body vibration training versus fitness training on muscle strength and muscle mass in older men: a 1-year randomized controlled trial. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2007;62:630–635. doi: 10.1093/gerona/62.6.630. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

