Preliminary study on the efficacy of xerostomia treatment with sialocentesis targeting thyroid disease patients given radioiodine therapy
- PMID: 31544098
- PMCID: PMC6728110
- DOI: 10.1186/s40902-019-0223-3
Preliminary study on the efficacy of xerostomia treatment with sialocentesis targeting thyroid disease patients given radioiodine therapy
Abstract
Background: Radioiodine therapy has been widely used for thyroid disease patients, but hyposalivation and xerostomia may occur in 10~30% of patients. Sialocentesis is a procedure that removes inflammatory substances in the salivary duct and expands the duct for the secretion and delivery of saliva. In this study, thyroid disease patients treated with radioactive iodine were selected among the patients with xerostomia who visited the hospital, and the effect of sialocentesis was compared and analyzed. And then, comparison between the radioiodine therapy-experienced group and the non-radioiodine therapy-experienced group was conducted.
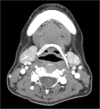
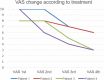
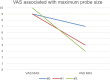
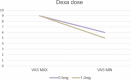
Results: In this study, we studied xerostomia patients who underwent radioiodine therapy due to thyroid diseases and who underwent sialocentesis at the Korea University Anam Hospital. Sialocentesis is conducted by one surgeon. The study also compares the clinical symptoms before and after the surgery. After the procedure, the discomfort due to xerostomia was reduced, and the symptom was improved effectively.
Conclusions: The results of this study showed that sialocentesis has a clinical effect in the treatment of xerostomia, which is a side effect of radioiodine therapy. In addition, the possibility of further clinical application of sialocentesis in the future is found.
Keywords: Radioiodine; Sialendoscopy; Sialocentesis; Submandibular gland; Xerostomia.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Rigler R, Scanlon P (1955) Radiation parotitis from radioactive iodine therapy. In: Proceedings of the staff meetings. Mayo Clinic - PubMed
-
- Solans R, Bosch J-A, Galofré P, Porta F, Roselló J, Selva-O’Callagan A, et al. Salivary and lacrimal gland dysfunction (sicca syndrome) after radioiodine therapy. J Nuclear Med. 2001;42(5):738–743. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources