1,25(OH)2D3 improves blood lipid metabolism, liver function, and atherosclerosis by constraining the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway in rats with hyperlipidemia
- PMID: 31544583
- PMCID: PMC6816365
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1669389
1,25(OH)2D3 improves blood lipid metabolism, liver function, and atherosclerosis by constraining the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway in rats with hyperlipidemia
Retraction in
-
Statement of Retraction: 1,25(OH)2D3 improves blood lipid metabolism, liver function, and atherosclerosis by constraining the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway in rats with hyperlipidemia.Cell Cycle. 2022 Jul;21(13):1437. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2066295. Epub 2022 Apr 22. Cell Cycle. 2022. PMID: 35451937 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
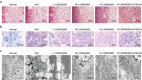
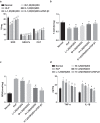
1,25(OH)2D3 has already been reported to function in some diseases. However, its role in hyperlipidemia (HLP) remains unknown. This study aims to investigate the effect of 1,25(OH)2D3 on HLP rats. Rat models were established by high-fat diet feeding, perfusion of different doses of 1,25-(OH)2D3 and injection of TGF-β1 siRNA. Whole blood viscosity, plasma viscosity, hematocrit, and erythrocyte aggregation index were detected, together with levels of biochemical indexes, 6-keto-PGF1α, and TXB2 in serum. Levels of oxidative stress indexes and inflammatory factors in serum and liver tissues were determined. TGF-β1 and Smad3 expression in serum, liver tissues, and aorta was detected. 1,25(OH)2D3 lowered HLP-induced rise of whole blood viscosity, red blood cell aggregation index, plasma viscosity, and hematocrit, TC, TG, LDL-C, apoB, ALT, AST, TXB2, MDA, IL-1β, TNF-α, and increased HLP-induced decrease of HDL-C, apoAI, 6-keto-PGF1α, SOD, GSH-Px, CAT, and T-AOC. TGF-β1 and Smad3 expression in serum, liver tissue, and aorta of 1,25(OH)2D3-treated rats reduced. High 1,25(OH)2D3 dose and inhibited TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway alleviated lipid metabolism, liver function, and atherosclerotic injury in HLP rats. Our study found that 1,25(OH)2D3 improves blood lipid metabolism, liver function, and atherosclerosis injury by constraining the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway in rats with HLP.
Keywords: 1; 25(OH)D; TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway; lipid metabolism.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Effects of oral selenium and magnesium co-supplementation on lipid metabolism, antioxidative status, histopathological lesions, and related gene expression in rats fed a high-fat diet.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Jul 21;17(1):165. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0815-4. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 30031400 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of 1,25-(OH)2D3 supplementation during gestation and lactation on TGF-β1 and Smad3 expression in lungs of rat offspring with asthma].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2012 May;14(5):366-70. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22613109 Chinese.
-
[Difference of lipid-lowering efficacy of "Xinjianqu" before and after fermentation and its mechanism based on LKB1-AMPK pathway and 16S rDNA sequencing technology].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023 Apr;48(8):2146-2159. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230112.301. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37282903 Chinese.
-
Effects of an aqueous extract of Crataegus pinnatifida Bge. var. major N.E.Br. fruit on experimental atherosclerosis in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Jul 9;148(2):563-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.04.053. Epub 2013 May 16. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23685195
-
MicroRNA modulation of lipid metabolism and oxidative stress in cardiometabolic diseases.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Sep;64:31-9. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.07.014. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23871755 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Insulin Resistance and Vitamin D Deficiency: A Link Beyond the Appearances.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Mar 17;9:859793. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.859793. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35369303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exercise reduces hyperlipidemia-induced cardiac damage in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice via its effects against inflammation and oxidative stress.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 5;13(1):9134. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36145-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37277452 Free PMC article.
-
Antiatherosclerotic effects of corilagin via suppression of the LOX-1/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro.J Nat Med. 2022 Mar;76(2):389-401. doi: 10.1007/s11418-021-01594-y. Epub 2022 Jan 22. J Nat Med. 2022. PMID: 35064897
-
A novel LC-MS/MS method combined with derivatization for simultaneous quantification of vitamin D metabolites in human serum with diabetes as well as hyperlipidemia.RSC Adv. 2023 Nov 22;13(48):34157-34166. doi: 10.1039/d3ra05700c. eCollection 2023 Nov 16. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 38020011 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang Y, Wang Z, Jin G, et al. Regulating dyslipidemia effect of polysaccharides from Pleurotus ostreatus on fat-emulsion-induced hyperlipidemia rats. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;101:107–116. - PubMed
-
- Karr S. Epidemiology and management of hyperlipidemia. Am J Manag Care. 2017;23(9 Suppl):S139–S148. - PubMed
-
- Huang J, Yang G, Huang Y, et al. Inhibitory effects of 1,25(OH)2D3 on the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the downregulation of HDAC2. Oncol Rep. 2017;38(3):1845–1850. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
