Infusion Reactions Associated with the Medical Application of Monoclonal Antibodies: The Role of Complement Activation and Possibility of Inhibition by Factor H
- PMID: 31544866
- PMCID: PMC6698840
- DOI: 10.3390/antib7010014
Infusion Reactions Associated with the Medical Application of Monoclonal Antibodies: The Role of Complement Activation and Possibility of Inhibition by Factor H
Abstract
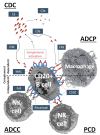
Human application of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), enzymes, as well as contrast media and many other particulate drugs and agents referred to as "nanomedicines", can initiate pseudoallergic hypersensitivity reactions, also known as infusion reactions. These may in part be mediated by the activation of the complement system, a major humoral defense system of innate immunity. In this review, we provide a brief outline of complement activation-related pseudoallergy (CARPA) in general, and then focus on the reactions caused by mAb therapy. Because the alternative pathway of complement activation may amplify such adverse reactions, we highlight the potential use of complement factor H as an inhibitor of CARPA.
Keywords: CARPA; complement; complement activation; factor H; hypersensitivity; infusion reaction; monoclonal antibody therapy; pseudoallergic reaction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Keating M.J., Flinn I., Jain V., Binet J.L., Hillmen P., Byrd J., Albitar M., Brettman L., Santabarbara P., Wacker B., et al. Therapeutic role of alemtuzumab (Campath-1H) in patients who have failed fludarabine: Results of a large international study. Blood. 2002;99:3554–3561. doi: 10.1182/blood.V99.10.3554. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

