Long Non-Coding RNA (LncRNA) UFC1/miR-34a Contributes to Proliferation and Migration in Breast Cancer
- PMID: 31544897
- PMCID: PMC6777379
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.917562
Long Non-Coding RNA (LncRNA) UFC1/miR-34a Contributes to Proliferation and Migration in Breast Cancer
Abstract
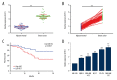
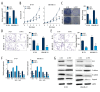
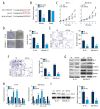
BACKGROUND At present, a number of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been realized as the critical regulators of breast cancers. Current evidence indicates that dysregulation of UFC1 contributes to the tumorigenesis and progression of various types of human cancer. However, the roles of UFC1 in breast cancer are still unclear. MATERIAL AND METHODS Firstly, we measured the expression of UFC1 in breast cancer tissues and cells lines compared with corresponding controls. Then, cell functional assays were performed to determine the roles of UFC1 in breast cancer progression in vitro. Moreover, the correlation between UFC1 and miR-34a was determined by luciferase reporter assays. Further, the role of miR-34a in regulating biological function of breast cancer and its downstream target CXCL10 was applied by a series of functional assays. RESULTS In present study, we found that UFC1 was highly expressed in breast tissue and cells lines compared with normal tissues and cell lines. Silenced UFC1 suppressed multiple biological activities of breast cancer cells, which also functioned as a miR-34a sponge in breast cancer. Furthermore, over-expressing miR-34a could prominently suppress cell growth, invasion, migration and inducing apoptosis in breast cancer cells. In addition, we verified that miR-34a was a target of CXCL10 by bioinformatics analysis and luciferase reporter assay. CONCLUSIONS LncRNA UFC1 regulated biological activity of breast cancer via miR-34a/CXCL10 axis, providing a novel diagnosis biomarker and potential therapeutic target for breast cancer.
Figures
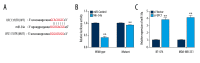
Similar articles
-
Dynamical Analysis of a Boolean Network Model of the Oncogene Role of lncRNA ANRIL and lncRNA UFC1 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Biomolecules. 2022 Mar 9;12(3):420. doi: 10.3390/biom12030420. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35327612 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA MNX1-AS1 promotes progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating miR-34a/SIRT1 axis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Aug;116:109029. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109029. Epub 2019 Jun 3. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31170665
-
MicroRNA-34a Inhibition of the TLR Signaling Pathway Via CXCL10 Suppresses Breast Cancer Cell Invasion and Migration.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46(3):1286-1304. doi: 10.1159/000489111. Epub 2018 Apr 16. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. Retraction in: Cell Physiol Biochem. 2020;54(5):1097. doi: 10.33594/000000299. PMID: 29689563 Retracted.
-
Expanding the Biotherapeutics Realm via miR-34a: "Potent Clever Little" Agent in Breast Cancer Therapy.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2019;20(8):665-673. doi: 10.2174/1389201020666190617162042. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31244419 Review.
-
Modification of miRNA Expression through plant extracts and compounds against breast cancer: Mechanism and translational significance.Phytomedicine. 2020 Mar;68:153168. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153168. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Phytomedicine. 2020. PMID: 31982837 Review.
Cited by
-
DARS-AS1 Knockdown Inhibits the Growth of Cervical Cancer Cells via Downregulating HMGB1 via Sponging miR-188-5p.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Jan-Dec;19:1533033820971669. doi: 10.1177/1533033820971669. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 33176595 Free PMC article.
-
Combined targeting of KRT23 and NCCRP1 as a potential novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer.Gland Surg. 2022 Oct;11(10):1673-1682. doi: 10.21037/gs-22-486. Gland Surg. 2022. PMID: 36353580 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs: A Link between Mammary Gland Development and Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 15;23(24):15978. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415978. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal delivery of non-coding RNAs: a pathway to apoptosis regulation in lung cancer.Med Oncol. 2025 Jul 1;42(8):307. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02852-9. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40591081 Review.
-
MicroRNAs and Their Influence on the ZEB Family: Mechanistic Aspects and Therapeutic Applications in Cancer Therapy.Biomolecules. 2020 Jul 12;10(7):1040. doi: 10.3390/biom10071040. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32664703 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Froehlich K, Schmidt A, Heger JI, et al. Breast cancer, placenta and pregnancy. Eur J Cancer. 2019;115:68–78. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359–86. - PubMed
-
- Damon LE, Cadman EC. The metabolic basis for combination chemotherapy. Pharmacol Ther. 1988;38:73–127. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

