Nanomaterial-based blood-brain-barrier (BBB) crossing strategies
- PMID: 31546096
- PMCID: PMC6915305
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119491
Nanomaterial-based blood-brain-barrier (BBB) crossing strategies
Abstract
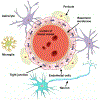
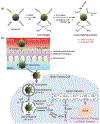
Increasing attention has been paid to the diseases of central nervous system (CNS). The penetration efficiency of most CNS drugs into the brain parenchyma is rather limited due to the existence of blood-brain barrier (BBB). Thus, BBB crossing for drug delivery to CNS remains a significant challenge in the development of neurological therapeutics. Because of the advantageous properties (e.g., relatively high drug loading content, controllable drug release, excellent passive and active targeting, good stability, biodegradability, biocompatibility, and low toxicity), nanomaterials with BBB-crossability have been widely developed for the treatment of CNS diseases. This review summarizes the current understanding of the physiological structure of BBB, and provides various nanomaterial-based BBB-crossing strategies for brain delivery of theranostic agents, including intranasal delivery, temporary disruption of BBB, local delivery, cell penetrating peptide (CPP) mediated BBB-crossing, receptor mediated BBB-crossing, shuttle peptide mediated BBB-crossing, and cells mediated BBB-crossing. Clinicians, biologists, material scientists and chemists are expected to be interested in this review.
Keywords: Blood-brain barrier (BBB); Central nervous system (CNS); Drug delivery systems; Nanomaterials.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures








References
-
- Nazem A, Mansoori GA, Nanotechnology solutions for Alzheimer’s disease: advances in research tools, diagnostic methods and therapeutic agents. J. Alzheimer’s Dis 13 (2008) 199223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

