Clinical, ultrasonographic and optical coherence tomography correlation of optic nerve head cupping in glaucoma patients
- PMID: 31546504
- PMCID: PMC6786225
- DOI: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_24_19
Clinical, ultrasonographic and optical coherence tomography correlation of optic nerve head cupping in glaucoma patients
Abstract
Purpose: To ascertain if ultrasound (USG) B-scan examination of the optic nerve head (ONH) can be a useful tool to diagnose and quantify glaucomatous cupping.
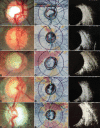
Methods: A cross-sectional observational study of 48 eyes of 48 patients with clear ocular media and cup-disc ratio of (CDR) ≥0.6 were included. The disc was studied by + 90D examination, USG B-scan and ONH Optical coherence tomography (OCT) by three masked observers. Observer-1 assessed the clinical CDR, observer-2recordedopticcup diameter on USG B-scan and observer-3performed ONH OCT to note the software computed average CDR. Measurements of cupping obtained by these 3 methods were compared and their relative strengths determined. The interdependency between variables was further studied using regression analysis.
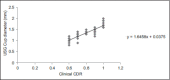
Results: Clinically assessed disc ratios of 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, and total corresponded to USG cup measures of 1.02 ± 0.11 mm, 1.23 ± 0.14 mm, 1.35 ± 0.072 mm, 1.45 ± 0.084 mm, 1.75 ± 0.15 mm and OCT average CDR of 0.62 ± 0.087, 0.68 ± 0.060, 0.75 ± 0.078, 0.81 ± 0.036, 0.89 ± 0.038, respectively. There was an excellent correlation between the three arms, with Pearson's co-efficient (r) of 0.87, P < 0.001 between clinical and USG cupping; r = 0.89, P < 0.001 between clinical and OCT cupping; and r = 0.88, P < 0.001 between USG and OCT cupping. A relation of y = 1.64x + 0.03 was obtained between them, where y stands for USG cup diameter and x stands for the observed clinical CDR.
Conclusion: Ultrasonographic measurement of optic cup diameter corresponds well to clinical ONH cupping. Therefore, it can reliably be used in quantifying ONH cupping in cases of media opacities which preclude optic disc visualization.
Keywords: B scan ultrasound; optic nerve head cupping; optical coherence tomography.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lamina Cribrosa Depth is Associated With the Cup-to-Disc Ratio in Eyes With Large Optic Disc Cupping and Cup-to-Disc Ratio Asymmetry.J Glaucoma. 2016 May;25(5):e536-45. doi: 10.1097/IJG.0000000000000387. J Glaucoma. 2016. PMID: 26859358
-
Optic Nerve Head Measurements With Optical Coherence Tomography: A Phantom-Based Study Reveals Differences Among Clinical Devices.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016 Jul 1;57(9):OCT413-20. doi: 10.1167/iovs.15-18738. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016. PMID: 27409500 Free PMC article.
-
Cupping reversal in pediatric glaucoma--evaluation of the retinal nerve fiber layer and visual field.Am J Ophthalmol. 2014 Nov;158(5):905-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2014.07.030. Epub 2014 Jul 25. Am J Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 25068638
-
The connective tissue phenotype of glaucomatous cupping in the monkey eye - Clinical and research implications.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2017 Jul;59:1-52. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2017.03.001. Epub 2017 Mar 12. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2017. PMID: 28300644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ophthalmic imaging for the diagnosis and monitoring of glaucoma: A review.Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2022 Mar;50(2):183-197. doi: 10.1111/ceo.14044. Epub 2022 Feb 5. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35050529 Review.
Cited by
-
Incidence and risk factors for post-penetrating keratoplasty glaucoma.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2022 Apr;70(4):1239-1245. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_1470_21. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35326024 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anand R, Gupta A, Ram J, Singh U, Kumar R. Visual outcome following cataract surgery in rural Punjab. India J Ophthalmol. 2000;48:153. - PubMed
-
- Jain AK, Sukhija J, Gupta A. ProTon tonometer determination of intraocular pressure in patients with scarred corneas. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2006;54:95–8. - PubMed
-
- Sihota R, Selvan H, Sharma A, Gupta A, Gupta V, Dada T, et al. Long-term evaluation of ocular hypertension with primary angle closure and primary open angles. Int Ophthalmol. 2019;39:803–12. - PubMed
-
- Anderson DR, Hendrickson A. Effect of intraocular pressure on rapid axoplasmic transport in monkey optic nerve. Invest Ophthalmol. 1974;13:771–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

