Isolation of a Pericentromeric Satellite DNA Family in Chnootriba argus (Henosepilachna argus) with an Unusual Short Repeat Unit (TTAAAA) for Beetles
- PMID: 31546864
- PMCID: PMC6780895
- DOI: 10.3390/insects10090306
Isolation of a Pericentromeric Satellite DNA Family in Chnootriba argus (Henosepilachna argus) with an Unusual Short Repeat Unit (TTAAAA) for Beetles
Abstract
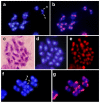
Ladybird beetles (Coccinellidae) are one of the largest groups of beetles. Among them, some species are of economic interest since they can act as a biological control for some agricultural pests whereas other species are phytophagous and can damage crops. Chnootriba argus (Coccinellidae, Epilachnini) has large heterochromatic pericentromeric blocks on all chromosomes, including both sexual chromosomes. Classical digestion of total genomic DNA using restriction endonucleases failed to find the satellite DNA located on these heterochromatic regions. Cloning of C0t-1 DNA resulted in the isolation of a repetitive DNA with a repeat unit of six base pairs, TTAAAA. The amount of TTAAAA repeat in the C. argus genome was about 20%. Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) analysis and digestion of chromosomes with the endonuclease Tru9I revealed that this repetitive DNA could be considered as the putative pericentromeric satellite DNA (satDNA) in this species. The presence of this satellite DNA was tested in other species of the tribe Epilachnini and it is also present in Epilachna paenulata. In both species, the TTAAAA repeat seems to be the main satellite DNA and it is located on the pericentromeric region on all chromosomes. The size of this satDNA, which has only six base pairs is unusual in Coleoptera satellite DNAs, where satDNAs usually have repeat units of a much larger size. Southern hybridization and FISH proved that this satDNA is conserved in some Epilachnini species but not in others. This result is in concordance with the controversial phylogenetic relationships among the genera of the tribe Epilachnini, where the limits between genera are unclear.
Keywords: C0t-1 DNA; Coccinellidae; Coleoptera; bryony ladybird; heterochromatin; in situ hybridization; satellite DNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Slipinski A., Tomaszewska W. Revision of the family Cavognathidae (Coleoptera: Cucujoidea) Aust. J. Entomol. 2010;49:256–267. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-6055.2010.00762.x. - DOI
-
- Howard N.F. Feeding of the Mexican bean beetle larva. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1941;34:766–769. doi: 10.1093/aesa/34.4.766. - DOI
-
- Katakura H., Nakano S., Kahono S., Abbas I., Noerdjito W.A., Nakamura K. Epilachnine ladybird beetles (Coleoptera: Coccineliidae) of West Sumatra and West Java. In: Nakamura K., Katakura H., editors. Evolutionary Biology and Population Dynamics of Herbivorous Lady Beetles in Indonesia. Published by editors; Sapporo, Japan: 1992. pp. 2–21.
-
- Das R., Mandal S.K., Maity T.K. Insect pollinators of pointed gourd and effect of different artificial methods of pollination on fruit setting and subsequent development of fruits. Veg. Sci. 2009;36:353–355.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

