Regulatory Effects and Interactions of the Wnt and OPG-RANKL-RANK Signaling at the Bone-Cartilage Interface in Osteoarthritis
- PMID: 31546898
- PMCID: PMC6769977
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20184653
Regulatory Effects and Interactions of the Wnt and OPG-RANKL-RANK Signaling at the Bone-Cartilage Interface in Osteoarthritis
Abstract
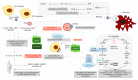
Cartilage and the bordering subchondral bone form a functionally active regulatory interface with a prominent role in osteoarthritis pathways. The Wnt and the OPG-RANKL-RANK signaling systems, as key mediators, interact in subchondral bone remodeling. Osteoarthritic osteoblasts polarize into two distinct phenotypes: a low secretory and an activated, pro-inflammatory and anti-resorptive subclass producing high quantities of IL-6, PGE2, and osteoprotegerin, but low levels of RANKL, thus acting as putative effectors of subchondral bone sclerosis. Wnt agonists, Wnt5a, Wisp-1 initiate excessive bone remodeling, while Wnt3a and 5a simultaneously cause loss of proteoglycans and phenotype shift in chondrocytes, with decreased expression of COL2A, aggrecan, and Sox-9. Sclerostin, a Wnt antagonist possesses a protective effect for the cartilage, while DKK-1 inhibits VEGF, suspending neoangiogenesis in the subchondral bone. Experimental conditions mimicking abnormal mechanical load, the pro-inflammatory milieu, but also a decreased OPG/RANKL ratio in the cartilage, trigger chondrocyte apoptosis and loss of the matrix via degradative matrix metalloproteinases, like MMP-13 or MMP-9. Hypoxia, an important cofactor exerts a dual role, promoting matrix synthesis via HIF-1α, a Wnt silencer, but turning on HIF-2α that enhances VEGF and MMP-13, along with aberrant collagen expression and extracellular matrix deterioration in the presence of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Keywords: Wnt signaling; bone-cartilage interface; osteoarthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

