Successful Treatments and Management of A Case of Canine Melioidosis
- PMID: 31547534
- PMCID: PMC6958349
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci6040076
Successful Treatments and Management of A Case of Canine Melioidosis
Abstract
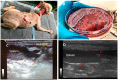
This communication presents a successful story of an attempt to treat and manage a case of canine melioidosis, a severe tropical disease caused by Burkholderia pseudomallei. A 10-year-old dog was trapped with barbed wires, causing an infected wound around its neck and back, which was later diagnosed as severe melioidosis. The dog was treated based on a modified human protocol. Intravenous meropenem injections (20 mg/kg twice daily) were given for 14 days to prevent death from sepsis prior to treatment with oral sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim (25 mg/kg twice daily) for 20 weeks to eliminate the bacteria. Canine melioidosis is an unusual infection in dogs, even in Thailand where melioidosis is highly endemic. This successful case management was solely based on proper diagnosis and appropriate treatments.
Keywords: Burkholderia pseudomallei; canine melioidosis; meropenem; sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funder had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Limmathurotsakul D., Dance D.A., Wuthiekanun V., Kaestli M., Mayo M., Warner J., Wagner D.M., Tuanyok A., Wertheim H., Yoke Cheng T., et al. Systematic review and consensus guidelines for environmental sampling of Burkholderia pseudomallei. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013;7:e2105. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002105. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Godoy D., Randle G., Simpson A.J., Aanensen D.M., Pitt T.L., Kinoshita R., Spratt B.G. Multilocus Sequence Typing and Evolutionary Relationships among the Causative Agents of Melioidosis and Glanders, Burkholderia pseudomallei and Burkholderia mallei. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003;41:2068–2079. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.5.2068-2079.2003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

