Advances in Treatment of Brominated Hydrocarbons by Heterogeneous Catalytic Ozonation and Bromate Minimization
- PMID: 31547554
- PMCID: PMC6803844
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24193450
Advances in Treatment of Brominated Hydrocarbons by Heterogeneous Catalytic Ozonation and Bromate Minimization
Abstract
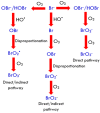
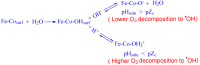
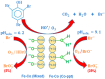
The formation of carcinogenic bromate ions is a constraint when ozone is used for the remediation of water containing brominated organic materials. With its strong oxidizing ability, ozone rapidly transforms bromide in aqueous media to bromate, through a series of reactions involving hydroxyl radicals. Several strategies, such as limiting the ozone concentration, maintaining pH < 6, or the use of ammonia or hydrogen peroxide were explored to minimize bromate generation. However, most of the above strategies had a negative effect on the ozonation efficiency. The advanced oxidation processes, using catalysts together with ozone, have proven to be a promising technology for the degradation of pollutants in wastewater, but very few studies have been conducted to find ways to minimize bromate formation during this approach. The proposed article, therefore, presents a comprehensive review on recent advances in bromate reduction in water by catalytic ozonation and proposes reaction mechanisms associated with the catalytic process. The main aim is to highlight any gaps in the reported studies, thus creating a platform for future research and a quest to find environment friendly and efficacious catalysts for minimizing bromate formation in aqueous media during ozonation of brominated organic compounds.
Keywords: bromate minimization; bromide; catalytic ozonation; metal oxides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
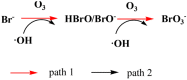

Similar articles
-
Critical Review on Bromate Formation during Ozonation and Control Options for Its Minimization.Environ Sci Technol. 2023 Nov 28;57(47):18393-18409. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.3c00538. Epub 2023 Jun 26. Environ Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 37363871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Reducing bromate formation by catalyzed ozonation].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2008 Jan;29(1):99-103. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2008. PMID: 18441924 Chinese.
-
Implications of bromate depression from H2O2 addition during ozonation of different bromide-bearing source waters.Chemosphere. 2020 Aug;252:126596. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126596. Epub 2020 Mar 25. Chemosphere. 2020. PMID: 32240859
-
Bromate minimization during ozonation: mechanistic considerations.Environ Sci Technol. 2001 Jun 15;35(12):2525-31. doi: 10.1021/es001502f. Environ Sci Technol. 2001. PMID: 11432558
-
Fate and reduction of bromate formed in advanced water treatment ozonation systems: A critical review.Chemosphere. 2021 Mar;266:128964. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128964. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Chemosphere. 2021. PMID: 33250222 Review.
Cited by
-
Ecological impacts of ballast water loading and discharge: insight into the toxicity and accumulation of disinfection by-products.Heliyon. 2022 Mar 13;8(3):e09107. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09107. eCollection 2022 Mar. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 35309395 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Neal C., Neal M., Hughes S., Wickham H., Hill L., Harman S. Bromine and bromide in rainfall, cloud, stream and groundwater in the Plynlimon area of mid-Wales. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007;11:301–312. doi: 10.5194/hess-11-301-2007. - DOI
-
- Flury M., Papritz A. Bromide in the natural environment: Occurrence and toxicity. J. Environ. Qual. 1993;22:747–758. doi: 10.2134/jeq1993.00472425002200040017x. - DOI
-
- Yuita K. Iodine, bromine and chlorine contents in soils and plants of Japan. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1983;29:403–428. doi: 10.1080/00380768.1983.10434645. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

