NT5E/CD73 as Correlative Factor of Patient Survival and Natural Killer Cell Infiltration in Glioblastoma
- PMID: 31547570
- PMCID: PMC6832588
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm8101526
NT5E/CD73 as Correlative Factor of Patient Survival and Natural Killer Cell Infiltration in Glioblastoma
Abstract
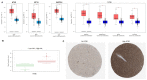
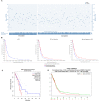
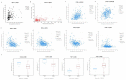
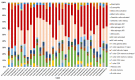
CD73, a cell-surface protein encoded by the gene NT5E, is overexpressed in glioblastoma (GBM), where it contributes to the tumor's pathophysiology via the generation of immunosuppressive adenosine. Adenosinergic signaling, in turn, drives immunosuppression of natural killer (NK) cells through metabolic and functional reprogramming. The correlation of CD73 with patient survival in relation to GBM pathology and the intratumoral infiltration of NK cells has not been comprehensively studied before. Here, we present an analysis of the prognostic relevance of CD73 in GBM based on transcriptional gene expression from patient data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. Utilizing bioinformatics data mining tools, we explore the relationship between GBM prognosis, NT5E expression, and intratumoral presence of NK cells. Our analysis demonstrates that CD73 is a negative prognostic factor for GBM and that presence of NK cells may associate with improved prognosis. Moreover, the interplay between expression of NT5E and specific NK genes hints to potential functional effects of CD73 on NK cell activation.
Keywords: CD73; adenosine; glioblastoma; immunometabolism; natural killer cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

