The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Thirty-sixth adult lung and heart-lung transplantation Report-2019; Focus theme: Donor and recipient size match
- PMID: 31548030
- PMCID: PMC6816340
- DOI: 10.1016/j.healun.2019.08.001
The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Thirty-sixth adult lung and heart-lung transplantation Report-2019; Focus theme: Donor and recipient size match
Figures
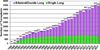
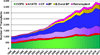
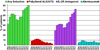


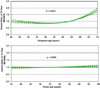









References
-
- Chambers DC, Cherikh WS, Goldfarb SB, et al. The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: thirty-fifth adult lung and heart-lung transplant report-2018; Focus theme: multiorgan Transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2018;37:1169–83. - PubMed
-
- Goldfarb SB, Hayes D Jr, Levvey BJ, et al. The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation.: twenty-first pediatric lung and heart–lung transplantation report-2018; focus theme: multiorgan transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2018;37:1196–206. - PubMed
-
- Rossano JW, Cherikh WS, Chambers DC, et al. The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: twenty-first pediatric heart transplantation report-2018; Focus theme: multiorgan Transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2018;37:1184–95. - PubMed
-
- Khush KK, Cherikh WS, Chambers DC, et al. The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: thirty-fifth adult heart transplantation Report-2018; focus theme: multiorgan transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2018;37:1155–68. - PubMed
-
- Yusen RD, Edwards LB, Kucheryavaya AY, et al. The Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: thirty-first adult lung and heart-lung transplant report—2014; focus theme: retransplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2014;33:1009–24. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

