Co-occurring Alterations in the RAS-MAPK Pathway Limit Response to MET Inhibitor Treatment in MET Exon 14 Skipping Mutation-Positive Lung Cancer
- PMID: 31548343
- PMCID: PMC6980768
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-1667
Co-occurring Alterations in the RAS-MAPK Pathway Limit Response to MET Inhibitor Treatment in MET Exon 14 Skipping Mutation-Positive Lung Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Although patients with advanced-stage non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC) harboring MET exon 14 skipping mutations (METex14) often benefit from MET tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) treatment, clinical benefit is limited by primary and acquired drug resistance. The molecular basis for this resistance remains incompletely understood.
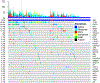
Experimental design: Targeted sequencing analysis was performed on cell-free circulating tumor DNA obtained from 289 patients with advanced-stage METex14-mutated NSCLC.
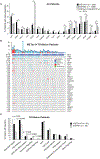
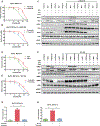
Results: Prominent co-occurring RAS-MAPK pathway gene alterations (e.g., in KRAS, NF1) were detected in NSCLCs with METex14 skipping alterations as compared with EGFR-mutated NSCLCs. There was an association between decreased MET TKI treatment response and RAS-MAPK pathway co-occurring alterations. In a preclinical model expressing a canonical METex14 mutation, KRAS overexpression or NF1 downregulation hyperactivated MAPK signaling to promote MET TKI resistance. This resistance was overcome by cotreatment with crizotinib and the MEK inhibitor trametinib.
Conclusions: Our study provides a genomic landscape of co-occurring alterations in advanced-stage METex14-mutated NSCLC and suggests a potential combination therapy strategy targeting MAPK pathway signaling to enhance clinical outcomes.
©2019 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures

References
-
- Frampton GM, Ali SM, Rosenzweig M, Chmielecki J, Lu X, Bauer TM, et al. Activation of MET via diverse exon 14 splicing alterations occurs in multiple tumor types and confers clinical sensitivity to MET inhibitors. Cancer Discov 2015;5(8):850–9. - PubMed
-
- Paik PK, Veillon R, Cortot A, Felip E, Sakai H, Mazieres J, et al. Phase II study of tepotinib in NSCLC patients with METex14 mutations. J Clin Oncol 2019;37(suppl; abstr 9005).
-
- Drilon AC, J. W, Weiss J, Ou I, Camidge R, Solomon B, Otterson GA, et al. Updated Antitumor Activity of Crizotinib in Patients with MET Exon 14-Altered Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. 2018. 9/25/18; Toronta, Canada.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 CA217882/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA239604/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA227807/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA224081/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA211052/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA210974/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA224068/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA217851/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA169338/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA204302/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 2018110/DDCF/Doris Duke Charitable Foundation/United States
- R01 CA230263/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

