Fibulin-4 exerts a dual role in LTBP-4L-mediated matrix assembly and function
- PMID: 31548410
- PMCID: PMC6789559
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1901048116
Fibulin-4 exerts a dual role in LTBP-4L-mediated matrix assembly and function
Erratum in
-
Correction for Kumra et al., Fibulin-4 exerts a dual role in LTBP-4L-mediated matrix assembly and function.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Dec 26;116(52):27159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1920843117. Epub 2019 Dec 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31843898 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
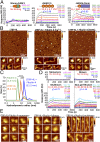
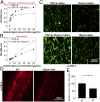
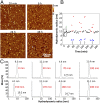
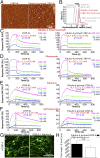
Elastogenesis is a hierarchical process by which cells form functional elastic fibers, providing elasticity and the ability to regulate growth factor bioavailability in tissues, including blood vessels, lung, and skin. This process requires accessory proteins, including fibulin-4 and -5, and latent TGF binding protein (LTBP)-4. Our data demonstrate mechanisms in elastogenesis, focusing on the interaction and functional interdependence between fibulin-4 and LTBP-4L and its impact on matrix deposition and function. We show that LTBP-4L is not secreted in the expected extended structure based on its domain composition, but instead adopts a compact conformation. Interaction with fibulin-4 surprisingly induced a conformational switch from the compact to an elongated LTBP-4L structure. This conversion was only induced by fibulin-4 multimers associated with increased avidity for LTBP-4L; fibulin-4 monomers were inactive. The fibulin-4-induced conformational change caused functional consequences in LTBP-4L in terms of binding to other elastogenic proteins, including fibronectin and fibrillin-1, and of LTBP-4L assembly. A transient exposure of LTBP-4L with fibulin-4 was sufficient to stably induce conformational and functional changes; a stable complex was not required. These data define fibulin-4 as a molecular extracellular chaperone for LTBP-4L. The altered LTBP-4L conformation also promoted elastogenesis, but only in the presence of fibulin-4, which is required to escort tropoelastin onto the extended LTBP-4L molecule. Altogether, this study provides a dual mechanism for fibulin-4 in 1) inducing a stable conformational and functional change in LTBP-4L, and 2) promoting deposition of tropoelastin onto the elongated LTBP-4L.
Keywords: LTBP-4; elastic fibers; fibrillin-1; fibronectin; fibulin-4.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kinsey R., et al. , Fibrillin-1 microfibril deposition is dependent on fibronectin assembly. J. Cell Sci. 121, 2696–2704 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Kantola A. K., Keski-Oja J., Koli K., Fibronectin and heparin binding domains of latent TGF-beta binding protein (LTBP)-4 mediate matrix targeting and cell adhesion. Exp. Cell Res. 314, 2488–2500 (2008). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

