Utility of a chemotherapy toxicity prediction tool for older patients in a community setting
- PMID: 31548802
- PMCID: PMC6726281
- DOI: 10.3747/co.26.4869
Utility of a chemotherapy toxicity prediction tool for older patients in a community setting
Abstract
Background: Expert groups have recommended incorporation of a geriatric assessment into clinical practice for older patients starting oncologic therapy. However, that practice is not standard primarily because of resource limitations. In the present study, we evaluated the effect on treatment decisions by oncologists in the community oncology setting of a brief geriatric assessment tool that estimates risk of toxicity.
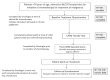
Methods: This prospective longitudinal study in 5 community oncology practices in British Columbia involved patients 70 years of age and older starting a new cytotoxic chemotherapy regimen. Clinical personnel completed a brief validated geriatric assessment tool-the Cancer and Aging Research Group chemotherapy toxicity tool (carg-tt)-that estimates the risk of grade 3 or greater toxicity in older patients. Physicians were asked if the carg-tt changed their treatment plan or prompted extra supports. Patients were followed to assess the incidence of toxicity during treatment.
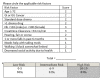
Results: The study enrolled 199 patients between July 2016 and February 2018. Mean age was 77 years. Treatment was palliative in 61.4% of the group. Compared with physician judgment, the carg-tt predicted higher rates of toxicity. In 5 patients, treatment was changed based on the carg-tt. In 38.5% of the patients, data from the tool prompted extra supports. Within the first 3 cycles of treatment, 21.3% of patients had experienced grade 3 or greater toxicity.
Conclusions: This study demonstrates that use of a brief geriatric assessment tool is possible in a broad community oncology practice. The tool modified the oncologist's supportive care plan for a significant number of older patients undertaking cytotoxic chemotherapy.
Keywords: Geriatric oncology; chemotherapy; elderly patients; geriatric assessment; toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST DISCLOSURES We have read and understood Current Oncology’s policy on disclosing conflicts of interest, and we declare that we have none.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predicting chemotherapy toxicity in older adults: Comparing the predictive value of the CARG Toxicity Score with oncologists' estimates of toxicity based on clinical judgement.J Geriatr Oncol. 2019 Mar;10(2):202-209. doi: 10.1016/j.jgo.2018.08.010. Epub 2018 Sep 14. J Geriatr Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30224184
-
Oncologists' perceptions on the usefulness of geriatric assessment measures and the CARG toxicity score when prescribing chemotherapy for older patients with cancer.J Geriatr Oncol. 2019 Mar;10(2):210-215. doi: 10.1016/j.jgo.2018.11.004. Epub 2018 Nov 28. J Geriatr Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30503312
-
The predictive value of G8 and the Cancer and aging research group chemotherapy toxicity tool in treatment-related toxicity in older Chinese patients with cancer.J Geriatr Oncol. 2021 May;12(4):557-562. doi: 10.1016/j.jgo.2020.10.013. Epub 2020 Oct 27. J Geriatr Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33127385
-
Elderly patients with advanced NSCLC: The value of geriatric evaluation and the feasibility of CGA alternatives in predicting chemotherapy toxicity.Pulmonology. 2019 Jan-Feb;25(1):40-50. doi: 10.1016/j.pulmoe.2018.07.004. Epub 2018 Sep 25. Pulmonology. 2019. PMID: 30266308 Review.
-
Comprehensive geriatric assessment in oncology.Interdiscip Top Gerontol. 2013;38:85-103. doi: 10.1159/000343608. Epub 2013 Jan 17. Interdiscip Top Gerontol. 2013. PMID: 23503518 Review.
Cited by
-
The Evolution of Geriatric Oncology and Geriatric Assessment over the Past Decade.Semin Radiat Oncol. 2022 Apr;32(2):98-108. doi: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2021.11.002. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35307123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Geriatric Assessment Tools in Head and Neck Radiation Oncology: An Unmet Need.Cureus. 2025 Mar 3;17(3):e79979. doi: 10.7759/cureus.79979. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40034421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predictive ability of the Cancer and Aging Research Group chemotherapy toxicity calculator in hematologic malignancy.J Geriatr Oncol. 2025 Jan;16(1):102144. doi: 10.1016/j.jgo.2024.102144. Epub 2024 Nov 5. J Geriatr Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39505607
-
Adjuvant Treatment of Elderly Breast Cancer Patients: Offer the Best Chances of Cure.Breast Care (Basel). 2022 Feb;17(1):71-80. doi: 10.1159/000513708. Epub 2021 Mar 4. Breast Care (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35355693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Geriatric assessment in older adults with non-Hodgkin lymphoma: A Young International Society of Geriatric Oncology (YSIOG) review paper.J Geriatr Oncol. 2022 Jun;13(5):572-581. doi: 10.1016/j.jgo.2022.02.005. Epub 2022 Feb 23. J Geriatr Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35216939 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

