Should sports and exercise medicine be taught in the Swiss undergraduate medical curricula? A survey among 1764 Swiss medical students
- PMID: 31548904
- PMCID: PMC6733322
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjsem-2019-000575
Should sports and exercise medicine be taught in the Swiss undergraduate medical curricula? A survey among 1764 Swiss medical students
Abstract
Objectives: The global lack of sports and exercise medicine (SEM) teaching at medical schools contrasts with evidence that physical activity (PA) plays a major role in preventing and treating non-communicable diseases (NCDs). The aims of this study were to (a) examine whether Swiss medical students are expected to acquire SEM-related skills and knowledge, (b) systematically reviewed SEM teaching in the Swiss undergraduate medical curricula, (c) assess if Swiss medical students are aware of SEM and (d) whether they would like SEM to be included in their curricula.
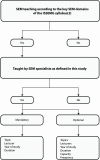
Methods: Two authors independently screened the 'Principal Relevant Objectives and Framework for Integrative Learning and Education in Switzerland' (PROFILES) for SEM-related learning objectives and reviewed the curricula. 7708 Swiss medical students were invited to participate in an online survey.
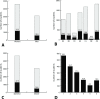
Results: 32 SEM-related learning objectives were identified in PROFILES with 20 of them linked to PA. Four of eight Swiss medical schools display limited mandatory SEM teachings. 1764 students participated in the survey (482.0% of the necessary sample size, 22.9% of all Swiss medical students). One in two students knew that SEM includes preventing and treating NCDs. Almost 95% of the participants would like SEM to be included in the curricula.
Conclusion: Despite its inclusion in PROFILES and comprehensive evidence that SEM should be taught at medical schools, this is scarcely the case in Switzerland. Swiss medical students have limited understanding of SEM, but are keen to have it included in the curricula. This study highlights the need for more comprehensive SEM teaching at Swiss medical schools.
Keywords: Switzerland; medical students; online survey; sports and exercise medicine; teaching; undergraduate.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: JC is a board member of the Swiss Society of Sports Medicine and the president of its junior section called ‘Students & Junior Doctors SGSM/SSMS’, LN is a board member of ‘Réseau Romand de la Médecine de l’Exercice et du Sport’, TP is a board member of the UK ‘Undergraduate Sports and Exericse Medicine Society’ and SK is a past president of the Swiss Society of Sports Medicine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Creating a sport and exercise medicine undergraduate syllabus: a delphi study.BMC Med Educ. 2023 Mar 23;23(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s12909-023-04139-x. BMC Med Educ. 2023. PMID: 36959591 Free PMC article.
-
How do Swiss medical schools prepare their students to become good communicators in their future professional careers: a questionnaire and interview study involving medical graduates, teachers and curriculum coordinators.BMC Med Educ. 2018 Nov 29;18(1):285. doi: 10.1186/s12909-018-1376-y. BMC Med Educ. 2018. PMID: 30497471 Free PMC article.
-
Complementary medicine courses in Swiss medical schools: actual status and students' experience.Swiss Med Wkly. 2010 Jan 23;140(3-4):44-51. doi: 10.4414/smw.2010.12760. Swiss Med Wkly. 2010. PMID: 20131118
-
Embedding sports and exercise medicine into the medical curriculum; a call for inclusion.BMC Med Educ. 2018 Dec 13;18(1):306. doi: 10.1186/s12909-018-1422-9. BMC Med Educ. 2018. PMID: 30545345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effects of flipped classrooms to improve learning outcomes in undergraduate health professional education: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2023 Jul 7;19(3):e1339. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1339. eCollection 2023 Sep. Campbell Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37425620 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Entrustable Professional Activities (EPAs) and milestones for MD sports medicine: A proposed portfolio.Med J Armed Forces India. 2021 Feb;77(Suppl 1):S129-S133. doi: 10.1016/j.mjafi.2020.12.026. Epub 2021 Feb 2. Med J Armed Forces India. 2021. PMID: 33612943 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise Science Graduates in the Healthcare System: A Comparison Between Australia and Switzerland.Front Sports Act Living. 2022 Mar 28;4:766641. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2022.766641. eCollection 2022. Front Sports Act Living. 2022. PMID: 35419518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Creating a sport and exercise medicine undergraduate syllabus: a delphi study.BMC Med Educ. 2023 Mar 23;23(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s12909-023-04139-x. BMC Med Educ. 2023. PMID: 36959591 Free PMC article.
-
High-intensity Interval Training for the Management of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: Participant Experiences and Perspectives.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2023 Oct 28;11(5):1050-1060. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2022.00091S. Epub 2023 Apr 21. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 37577222 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ergen E. Roots of sports medicine. Arch Med Deporte 2014;31:263–7.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
