JOIN trial: treatment outcome and recovery status of peripheral sensory neuropathy during a 3-year follow-up in patients receiving modified FOLFOX6 as adjuvant treatment for stage II/III colon cancer
- PMID: 31549217
- PMCID: PMC6820589
- DOI: 10.1007/s00280-019-03957-5
JOIN trial: treatment outcome and recovery status of peripheral sensory neuropathy during a 3-year follow-up in patients receiving modified FOLFOX6 as adjuvant treatment for stage II/III colon cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Adjuvant FOLFOX therapy is an established standard-of-care for resected colon cancer. Peripheral sensory neuropathy (PSN) is regarded as the major toxicity issue related to FOLFOX therapy. There have been a few reports on the recovery status from PSN thereafter. JOIN trial investigated the tolerability and efficacy of adjuvant modified FOLFOX6 (mFOLFOX6) in Japanese patients with stage II/III colon cancer.
Methods: Twelve cycles of mFOLFOX6 were given to patients with stage II/III curatively resected colon cancer. Treatment outcomes, including disease-free survival (DFS), relapse-free survival (RFS), overall survival (OS), and recovery status of PSN during 3-year follow-up, were investigated.
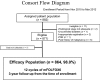
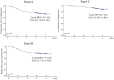
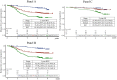
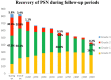
Results: Of the 882 patients enrolled from 2010 to 2012, 864 were eligible for the efficacy analyses. Three-year DFS, RFS, and OS were favorable in 92.1, 92.8, and 97.4% of stage II patients; 76.4, 77.9, and 93.8% of stage IIIA/B; and 61.6, 62.7, and 85.9% of stage IIIC, respectively. The cumulative incidence of PSN during treatment was 47.8% in grade 1 (G1), 30.3% in G2, and 5.8% in G3. For those with G3 PSN during treatment, there was gradual recovery in 1.1% of patients at 12 months after enrollment, 0.5% at 24 months, and 0.2% at 36 months. However, G1 or G2 residual PSN after 3 years was observed in 21.0% (18.7%, G1; 2.3%, G2).
Conclusions: Adjuvant mFOLFOX6 therapy was effective and well tolerated in patients with stage II/III colon cancer. Most patients recovered from G3 PSN related to oxaliplatin, but approximately 20% of patients had G1 or G2 PSN at 3-year follow-up.
Keywords: Colon cancer; Efficacy; Long-term peripheral sensory neuropathy; Modified FOLFOX6; Oxaliplatin.
Conflict of interest statement
T. Yoshino has received grants from MSD K.K., Sanofi K.K., Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma Co., Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., GlaxoSmithKline K.K., and Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd., and honoraria from Sanofi K.K., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K, and Merck Serono Co., Ltd. outside the submitted work; M. Kotaka has received honoraria from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Yakult Honsha Co., Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Merck Serono Co., Ltd., and Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. outside the submitted work; K. Shinozaki has received honoraria from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Mochida Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Merck Serono Co., Ltd., Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Yakult Honsha Co., Ltd., Astellas Pharma Inc., Novartis Pharma K.K., Eisai Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Shionogi & Co., Ltd., Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd., and Asahi Kasei Pharma Co. outside the submitted work; T. Touyama declares no conflicts of interest; D. Manaka declares no conflicts of interest; T. Matsui declares no conflicts of interest; K. Ishigure has received honoraria from ONO Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Yakult Honsha Co., Ltd. outside the submitted work; J. Hasegawa declares no conflicts of interest; K. Inoue declares no conflicts of interest; Y. Munemoto declares no conflicts of interest; A. Takagane declares no conflicts of interest; H. Ishikawa declares no conflicts of interest; H. Ishida has received personal fees from Asahi Kasei, Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. outside the submitted work; Y. Ogata declares no conflicts of interest; K. Oba has received personal fees from Eisai Co., Ltd., Bristol-Myers Squibb K.K., Merck Serono Japan, ONO Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Asahi Kasei, Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo, Inc. and Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. outside the submitted work; K. Goto has received grants and personal fees from Stemcentrx (now part of AbbVie), AstraZeneca K.K., Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb K.K., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo, Inc., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Life Technologies Japan Ltd., Merck Serono Co., Ltd., MSD K.K., Novartis Pharma K.K., ONO Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Pfizer Japan Inc., Riken Genesis Co., Ltd., Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., grants from Amgen Astellas BioPharma K.K., Astellas Pharma Inc., Eisai Co., Ltd., Ignyta Inc., Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd., Loxo Oncology, Inc., Oxonc, RTI Health Solutions, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma Co., Ltd., as well as personal fees from F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Nippon Kayaku Co., Ltd., Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and SRL Inc. outside the submitted work; J. Sakamoto has received consultant fees from Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., honoraria from Tsumura Co., Ltd., Nippon Kayaku Co., Ltd., and Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. outside the submitted work; Y. Maehara has received grants from Yakult Honsha Co., Ltd. outside the submitted work; A. Ohtsu has received grants and personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb K.K., personal fees from ONO Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. outside the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- NCCN guidelines for patients: colon cancer version 4 (2018) www.nccn.org. Accessed 5 Nov 2018
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

