The Effects of Laser Moxibustion on Knee Osteoarthritis Pain in Rats
- PMID: 31549920
- PMCID: PMC6978776
- DOI: 10.1089/photob.2019.4716
The Effects of Laser Moxibustion on Knee Osteoarthritis Pain in Rats
Abstract
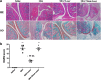
Background: Although chronic pain affects the quality of life of patients with osteoarthritis, current medical treatments are either ineffective or have long-term side effects. Recently, low-intensity laser irradiation of corresponding acupoints was demonstrated to alleviate pain. Objective: The aim of the present study was to investigate the effects of 10.6 μm laser moxibustion on a monosodium iodoacetate (MIA)-induced knee osteoarthritis pain model. Methods: Thirty-two rats were randomly assigned to four groups: Saline, MIA, MIA+Laser, and MIA+Sham Laser. The 10.6 μm laser was used to irradiate the ST35 for 10 min once a day for a total of seven applications. The paw withdrawal mechanical threshold and weight-bearing difference were performed to evaluate the analgesic effects of laser moxibustion. At the end of the experiment on days 28, the joint histology, the levels of metalloproteinases-13 (MMP-13) in the cartilage, and TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 in the synovial membrane were measured to determine the chondroprotection and anti-inflammatory effect of laser moxibustion. Results: Early laser moxibustion significantly reversed the MIA-induced mechanical hyperalgesia and weight-bearing difference, especially on the 28th day (p < 0.001). Moreover, laser moxibustion prevented the articular pathological lesions and cartilage destruction on days 28 (p < 0.01). Remarkably, the levels of cartilage MMP-13, and synovial TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 also decreased on day 28 (p < 0.05) after the early treatment of laser moxibustion. Conclusions: 10.6 μm laser moxibustion may have long-lasting analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and chondroprotection effects, suggesting that it may emerge as a potential therapeutic strategy for the chronic pain treatment of osteoarthritis.
Keywords: chronic pain; knee osteoarthritis; laser moxibustion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Hawker GA, Stewart L, French MR, et al. Understanding the pain experience in hip and knee osteoarthritis—an OARSI/OMERACT initiative. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2008;16:415–422 - PubMed
-
- McCoy AM. Animal models of osteoarthritis: comparisons and key considerations. Vet Pathol 2015;52:803–818 - PubMed
-
- Udo M, Muneta T, Tsuji K, et al. Monoiodoacetic acid induces arthritis and synovitis in rats in a dose- and time-dependent manner: proposed model-specific scoring systems. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2016;24:1284–1291 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

