Significantly Increased Patient Satisfaction Following Liquid Formulation AbobotulinumtoxinA Treatment in Glabellar Lines: FACE-Q Outcomes From a Phase 3 Clinical Trial
- PMID: 31550352
- PMCID: PMC7427150
- DOI: 10.1093/asj/sjz248
Significantly Increased Patient Satisfaction Following Liquid Formulation AbobotulinumtoxinA Treatment in Glabellar Lines: FACE-Q Outcomes From a Phase 3 Clinical Trial
Abstract
Background: The FACE-Q patient-reported outcome assesses patient experiences/outcomes with aesthetic facial procedure. A recent trial of abobotulinumtoxinA (ASI, liquid formulation) was the first to our knowledge to assess satisfaction with FACE-Q after glabellar line (GL) injection.
Objectives: The authors sought to evaluate patient satisfaction with ASI for GL treatment employing 3 FACE-Q scales: facial appearance, psychological well-being, and aging appearance.
Methods: This was a Phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (NCT02353871) of ASI 50 units in adults with moderate-to-severe GL with 6-month follow-up.
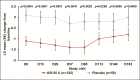
Results: Significantly greater least squares mean changes from baseline were associated with ASI treatment (N = 125) vs placebo (N = 59) for satisfaction with facial appearance at all visits until day 148 (5 months; P < 0.0001-0.0037), psychological well-being at all visits (P < 0.0001-0.0279), and aging appearance at all visits except day 148 (P < 0.0001-0.0409). Significant differences (ASI vs placebo) were observed at all visits for individual items: "how rested your face looks" (P < 0.0001-0.0415), "I feel okay about myself" (P = 0.0011-0.0399), and "I feel attractive" (P < 0.0001-0.0102). Maximal least squares mean (standard error) changes in aging appearance score were -1.4 (0.3; ASI) and -0.3 (0.4; placebo). Investigators' live assessment of GL at maximum frown significantly correlated with improvements in FACE-Q facial appearance and psychological scales (all patients: r = -0.41 and r = -0.36 [both P < 0.0001], respectively).
Conclusions: Significant improvements in patient satisfaction with aging, facial appearance, and, importantly, psychological well-being were demonstrated with ASI employing FACE-Q scales up to 5 to 6 months post-injection. Results support a long duration of efficacy with ASI and use of FACE-Q in future trials and clinical practice.
© 2019 The American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, Inc.
Figures


Comment in
-
Facial Line Outcomes (FLO-11) and Facial Line Satisfaction Questionnaire (FLSQ) Meet FDA Patient-Reported Outcome Guidance.Aesthet Surg J. 2020 Nov 19;40(12):NP710-NP711. doi: 10.1093/asj/sjaa101. Aesthet Surg J. 2020. PMID: 32539077 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Response to "Facial Line Outcomes (FLO-11) and Facial Line Satisfaction Questionnaire (FLSQ) Meet FDA PRO Guidance".Aesthet Surg J. 2020 Nov 19;40(12):NP708-NP709. doi: 10.1093/asj/sjaa240. Aesthet Surg J. 2020. PMID: 32960940 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery. ISAPS International Study on Aesthetic/Cosmetic Procedures Performed in 2017 2018. https://www.isaps.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/ISAPS_2017_Internationa... Accessed March 27, 2019.
-
- Kosowski TR, McCarthy C, Reavey PL, et al. . A systematic review of patient-reported outcome measures after facial cosmetic surgery and/or nonsurgical facial rejuvenation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;123(6):1819-1827. - PubMed
-
- Cox SE, Finn JC. Social implications of hyperdynamic facial lines and patient satisfaction outcomes. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 2005;45(3):13-24. - PubMed
-
- Cox SE, Finn JC, Stetler L, Mackowiak J, Kowalski JW. Development of the Facial Lines Treatment Satisfaction Questionnaire and initial results for botulinum toxin type A-treated patients. Dermatol Surg. 2003;29(5):444-449; discussion 449. - PubMed
-
- Carruthers J, Carruthers A. Botulinum toxin type A treatment of multiple upper facial sites: patient-reported outcomes. Dermatol Surg. 2007;33(1 Spec No): S10-S17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

