MC4R Is Involved in Neuropathic Pain by Regulating JNK Signaling Pathway After Chronic Constriction Injury
- PMID: 31551683
- PMCID: PMC6746920
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00919
MC4R Is Involved in Neuropathic Pain by Regulating JNK Signaling Pathway After Chronic Constriction Injury
Abstract
Background: Neuropathic pain can develop after nerve injury, when deleterious changes occur in injured neurons and glia cells. Melanocortin 4 receptor (MC4R) is involved in the regulation of pain due to its high expressions in brain. Moreover, MC4R could mediate the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling pathway, but whether the MC4R-regulated JNK signaling pathway participated in neuropathic pain after chronic constriction injury (CCI) is still unclear.
Methods: A total of 128 Sprague-Dawley rats were allocated into four experiment groups: the SHAM group, CCI + NaCl group, CCI + HS group, and CCI + SP + HS group. For the CCI + NaCl group, the sciatic nerves were ligated. For the SHAM group, an identical manner to the CCI without ligation was performed. For CCI + HS and CCI + SP + HS groups, rats were injected with MC4R inhibitor (HS014) and HS014 plus JNK inhibitor (SP600125), respectively, from days 3 to 14 after CCI. Paw withdrawal latency (PWL) and paw withdrawal threshold (PWT) were used to assess the nociceptive behavior. ELISA was used to detect the levels of inflammatory cytokines. qRT-PCR and Western blots (WB) were utilized to examine the mRNA and protein expressions of JNK signaling pathway-related genes. Meanwhile, the expression levels of MC4R and p-JNK were further evaluated by immunohistochemistry (IHC) and immunofluorescence (IF) experiments. Finally, in order to confirm the in vivo results, astrocytes were isolated and transfected with MC4R-overexpression plasmid. Furthermore, the protein expressions of JNK signaling pathway-related genes were tested by WB.
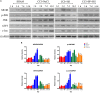
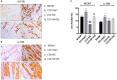
Results: It was showed that the values of PWL and PWT were significantly increased in CCI + HS group and CCI + SP + HS group compared with CCI + NaCl group. The increased interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-1β, and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) secretion in CCI + NaCl group was lowered by HS and SP + HS. MC4R, p-JNK, ATF3, and c-Jun levels were up-regulated with CCI surgery, but down-regulated with HS and SP + HS treatments. Moreover, the IHC and IF results further revealed that MC4R and p-JNK expressions in CCI + NaCl group were remarkably higher than those in HS group and HS + SP group. In vitro data also indicated that HS, SP, and SP + HS could down-regulate the expressions of MC4R, p-JNK, ATF3, and c-Jun in M1830 astrocytes.
Conclusion: Our findings indicated that MC4R is involved in neuropathic pain by regulating JNK signaling pathway after CCI.
Keywords: JNK signaling pathway; chronic constriction injury; melanocortin 4 receptor (MC4R); neuropathic pain; nociceptive behavior; paw withdrawal latency; paw withdrawal threshold.
Figures





References
-
- Birklein F. (2002). Mechanism-based treatment principles of neuropathic pain. Fortschr. Neurol. Psychiatr. 70 88–94. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

