Long Non-coding RNA TUG1 Sponges Mir-145a-5p to Regulate Microglial Polarization After Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation
- PMID: 31551710
- PMCID: PMC6748346
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00215
Long Non-coding RNA TUG1 Sponges Mir-145a-5p to Regulate Microglial Polarization After Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation
Abstract
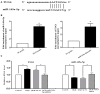
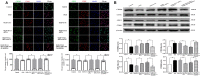
Microglia plays a critical role in neuroinflammation after ischemic stroke by releasing diverse inflammatory cytokines. Long non-coding RNA taurine up-regulated gene 1 (lncRNA TUG1) is widely expressed in adult brain and has been reported to participate in multiple biological processes associated with nervous system diseases. However, the role of TUG1 in microglial activation remains unidentified. BV-2 microglial cells were cultured in vitro and TUG1 siRNA was used to knock down its RNA level. Microglial cells were subjected to oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) for 4 h following TUG1 siRNA or scramble siRNA transient transfection. After 24 h reoxygenation, TUG1 level and microglial M1/M2 phenotype, as well as releasing inflammatory cytokines and their role to viability of SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells were determined by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR), ELISA, immunofluorescence and western blot. In addition, miR-145a-5p, a putative microRNA to bind with TUG1 by bioinformatics analysis, was simultaneously examined, then the interaction of TUG1 with miR-145a-5p and the potential involvement of NF-κB pathway were further evaluated by RNA-RNA pull-down assay and western blot. The cellular level of TUG1 was transiently up-regulated in microglial cells 24 h after OGD treatment, with an inverse correlation to downregulated miR-145a-5p. TUG1 knockdown drove microglial M1-like to M2-like phenotypic transformation with reduced production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (tumor necrosis factor-α, TNF-α; interleukin-6, IL-6) and incremental release of anti-inflammatory cytokine (interleukin-10, IL-10), as a result, promoted the survival of SH-SY5Y cells. Meanwhile, TUG1 knockdown prevented OGD-induced activation of NF-κB pathway as well, represented by decreased ratios of p-p65/p65 and p-IκBα/IκBα proteins. Furthermore, we found that TUG1 could physically bind to miR-145a-5p while miR-145a-5p inhibitor abolished the protective effects of TUG1 knockdown through activation of NF-κB pathway, suggesting a negative interaction between TUG1 and miR-145a-5p. Our study demonstrated that lncRNA TUG1, sponging miR-145a-5p with negative interaction, could regulate microglial polarization and production of inflammatory cytokines at a relatively early stage after OGD insult, where NF-κB pathway might be involved, possibly providing a promising therapeutic target against inflammatory injury.
Keywords: NF-κB signaling; inflammatory cytokines; microRNA-145a-5p; microglia; oxygen-glucose deprivation; phenotype; taurine up-regulated gene 1.
Figures



Similar articles
-
LncRNA Tug1 Contributes Post-stroke NLRP3 Inflammasome-Dependent Pyroptosis via miR-145a-5p/Tlr4 Axis.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Nov;59(11):6701-6712. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-03000-4. Epub 2022 Aug 22. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35989413
-
Down-regulation of taurine-up-regulated gene 1 attenuates inflammation by sponging miR-9-5p via targeting NF-κB1/p50 in multiple sclerosis.Life Sci. 2019 Sep 15;233:116731. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116731. Epub 2019 Aug 5. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31394128
-
LncRNA TUG1 Exacerbates Myocardial Fibrosis in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy by Modulating the microRNA-145a-5p/Cfl2 Axis.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 1;81(3):192-202. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000001391. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36450139
-
Long noncoding RNA SNHG16 targets miR-146a-5p/CCL5 to regulate LPS-induced WI-38 cell apoptosis and inflammation in acute pneumonia.Life Sci. 2019 Jul 1;228:189-197. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.05.008. Epub 2019 May 7. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31071307 Review.
-
The dual face of microglia (M1/M2) as a potential target in the protective effect of nutraceuticals against neurodegenerative diseases.Front Aging. 2023 Sep 6;4:1231706. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2023.1231706. eCollection 2023. Front Aging. 2023. PMID: 37744008 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Perspectives on Epigenetics Alterations Associated with Smoking and Vaping.Function (Oxf). 2021 Apr 23;2(3):zqab022. doi: 10.1093/function/zqab022. eCollection 2021. Function (Oxf). 2021. PMID: 35330676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Regulations of Microglia/Macrophage Polarization in Ischemic Stroke.Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 Oct 11;14:697416. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.697416. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34707480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long Non-coding RNAs as Promising Therapeutic Approach in Ischemic Stroke: a Comprehensive Review.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Apr;58(4):1664-1682. doi: 10.1007/s12035-020-02206-8. Epub 2020 Nov 24. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 33236327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long Non-coding RNA H19 Promotes NLRP3-Mediated Pyroptosis After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats.Transl Stroke Res. 2023 Dec;14(6):987-1001. doi: 10.1007/s12975-022-01104-6. Epub 2022 Nov 24. Transl Stroke Res. 2023. PMID: 36418735
-
LncRNA-TUG1 promotes the progression of infantile hemangioma by regulating miR-137/IGFBP5 axis.Hum Genomics. 2021 Aug 6;15(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s40246-021-00349-w. Hum Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34362467 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

