NMR Metabolomics and Random Forests Models to Identify Potential Plasma Biomarkers of Blood Stasis Syndrome With Coronary Heart Disease Patients
- PMID: 31551804
- PMCID: PMC6738169
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01109
NMR Metabolomics and Random Forests Models to Identify Potential Plasma Biomarkers of Blood Stasis Syndrome With Coronary Heart Disease Patients
Abstract
Background: Coronary heart disease (CHD) remains highly prevalent and is one of the largest causes of death worldwide. Blood stasis syndrome (BSS) is the main syndrome associated with CHD. However, the underlying biological basis of BSS with CHD is not yet been fully understood.
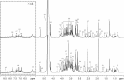
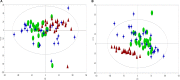
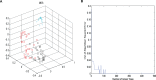
Materials and methods: We proposed a metabolomics method based on 1H-NMR and random forest (RF) models to elucidate the underlying biological basis of BSS with CHD. Firstly, 58 cases of CHD patients, including 27 BSS and 31 phlegm syndrome (PS), and 26 volunteers were recruited from Xiangya Hospital affiliated to Central South University. A 1 mL venous blood sample was collected for NMR analysis. Secondly, principal component analysis (PCA), partial least squares discrimination analysis (PLS-DA) and RF was applied to observe the classification of each group, respectively. Finally, RF and multidimensional scaling (MDS) were utilized to discover the plasma potential biomarkers in CHD patients and CHD-BSS patients.
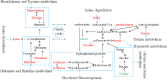
Results: The models constructed by RF could visually discriminate BSS from PS in CHD patients. Simultaneously, we obtained 12 characteristic metabolites, including lysine, glutamine, taurine, tyrosine, phenylalanine, histidine, lipid, citrate, choline, lactate, α-glucose, β-glucose related to the CHD patients, and Choline, β-glucose, α-glucose and tyrosine were considered as potential biomarkers of CHD-BSS.
Conclusion: The combining of 1H-NMR profiling with RF models was a useful approach to analyze complex metabolomics data (should be deleted). Choline, β-glucose, α-glucose and tyrosine were considered as potential biomarkers of CHD-BSS.
Keywords: Systems Biology; ZHENG types; blood stasis syndrome; coronary heart disease; metabolomics; random forests.
Figures

References
-
- Breiman L. (2001). Random forests. Mach. Learn. 45 5–21.
-
- Brindle J. T., Antti H., Holmes E., Tranter G., Nicholson J. K., Bethell H. W., et al. (2002). Rapid and noninvasive diagnosis of the presence and severity of coronary heart disease using 1H-NMR-based metabonomics. Nat. Med. 8 1439–1444. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

