Cardiotonic Pills Plus Recombinant Human Prourokinase Ameliorates Atherosclerotic Lesions in LDLR-/- Mice
- PMID: 31551808
- PMCID: PMC6747059
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01128
Cardiotonic Pills Plus Recombinant Human Prourokinase Ameliorates Atherosclerotic Lesions in LDLR-/- Mice
Abstract
Aim: This study was to explore the protective effects of cardiotonic pills (CP) or/and recombinant human prourokinase (proUK)on the atherosclerosis and the potential underlying mechanism.
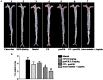
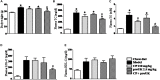
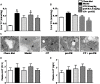
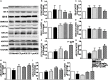
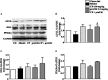
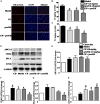
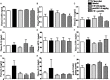
Methods and results: Atherosclerosis was induced in LDLR-/- mice by high fat diet contained 20% lard and 0.5% cholesterol. Daily oral administration of CP (130 mg/kg) or/and intravenous injection of proUK (2.5 mg/kg, twice a week) began at 8 weeks after feeding with high fat diet and continued for 4 weeks. CP alone treatment markedly decreased plasma triglyceride, but did not ameliorate atherosclerosis plaque. No effect was observed for proUK alone on any endpoints tested. CP plus proUK induced a significantly reduction in the atherosclerotic lesions, along with decreased levels of total cholesterol, triglyceride in the plasma. CP plus proUK inhibited the elevated hepatic total cholesterol and triglyceride in high fat diet-fed LDLR-/- mice, up-regulating the expressions of ATP-binding cassette gene 5 and 8, and adipose triglyceride lipase. In the aorta, CP plus proUK inhibited the expression of scavenger receptor A and CD36 in LDLR-/- mice. In addition, we observed that systemic inflammation was inhibited, manifested downregulation of plasma macrophage inflammatory protein-1α and intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1.
Conclusion: CP plus proUK effectively attenuated atherosclerosis plaque in LDLR-/- mice, which is associated with normalizing the lipid metabolism in the liver and aorta, reducing phagocytosis of receptor-mediated modified-LDL uptake and inhibiting systemic inflammation.
Keywords: ATP-binding cassette gene 8; CD36; adipose triglyceride lipase; atherosclerosis; inflammation; scavenger receptor A.
Figures

References
-
- Chen Y. L., Hu C. S., Lin F. Y., Chen Y. H., Sheu L. M., Ku H. H., et al. (2006). Salvianolic acid B attenuates cyclooxygenase-2 expression in vitro in LPS-treated human aortic smooth muscle cells and in vivo in the apolipoprotein-E-deficient mouse aorta. J. Cell. Biochem. 98 618–631. 10.1002/jcb.20793 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

