Changing Body Weight-Based Dosing to a Flat Dose for Avelumab in Metastatic Merkel Cell and Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma
- PMID: 31553054
- PMCID: PMC7027979
- DOI: 10.1002/cpt.1645
Changing Body Weight-Based Dosing to a Flat Dose for Avelumab in Metastatic Merkel Cell and Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma
Abstract
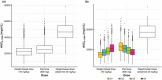
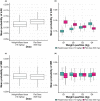
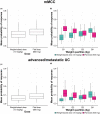
Avelumab, an anti-programmed death-ligand 1 monoclonal antibody approved for the treatment of metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma and platinum-treated urothelial carcinoma, was initially approved with a 10 mg/kg weight-based dose. We report pharmacokinetic (PK)/pharmacodynamic analyses for avelumab comparing weight-based dosing and a flat 800 mg dose, developed using data from 1,827 patients enrolled in 3 clinical trials (NCT01772004, NCT01943461, and NCT02155647). PK metrics were simulated for weight-based and flat-dosing regimens and summarized by quartiles of weight. Derived exposure metrics were used in simulations of exposure-safety (various tumors) and exposure-efficacy (objective responses; Merkel cell or urothelial carcinoma). Flat dosing was predicted to provide similar exposure to weight-based dosing, with slightly lower variability. Exposure-safety and exposure-efficacy simulations suggested similar benefit:risk profiles for the two dosing regimens. These pharmacometric analyses provided the basis for the US Food and Drug Administration approval of a flat dose of avelumab 800 mg every 2 weeks in approved indications.
© 2019 MERCK KGAA. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
A.M.N. and A.K. are employees of Merck KGaA. J.J.W. and J.R.W. were employed as consultants by Merck KGaA when analyses were performed. H.D. and B.N. are employees of EMD Serono, a business of Merck KGaA. S.B. and C.L.B. are employees of Pfizer Inc. P.G. is an employee of Merck Serono SA, Lausanne, Switzerland, an affiliate of Merck KGaA.
Figures
References
-
- Hargadon, K.M. , Johnson, C.E. & Williams, C.J. Immune checkpoint blockade therapy for cancer: an overview of FDA‐approved immune checkpoint inhibitors. Int. Immunopharmacol. 62, 29–39 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Stroh, M. et al. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of atezolizumab in metastatic urothelial carcinoma. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 102, 305–312 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

