Adjustable sling for the treatment of post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence: systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 31553360
- PMCID: PMC6748345
- DOI: 10.31744/einstein_journal/2019RW4508
Adjustable sling for the treatment of post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence: systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Urinary incontinence after prostatectomy has a significant negative impact on the quality of life of the patient. The surgical treatment includes several models of male slings, such as adjustable slings. The objective of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of adjustable sling in the treatment of post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence. This is a systematic review of literature. The following electronic databases were searched until January 2018: PubMed®, Embase, CENTRAL and LILACS. The keywords used in the search strategies were: "prostatectomy" [Mesh], "urinary incontinence" [Mesh] and "suburethral slings" [Mesh]. Randomized clinical trials and observational studies, with or without Control Group, and follow-up of more than 12 months were included. Only one randomized study with high risk of bias was included and it concluded the effectiveness equivalence between adjustable and non-adjustable slings. All other studies were cases series with patients of varying levels of incontinence intensity and history of pelvic radiation therapy and previous surgeries. The meta-analysis for 0 pad in 24 hours demonstrated an effectiveness of 53%. For the 0 to 1 pad test in 24 hours, the meta-analysis resulted in an effectiveness of 69%. Risk factors for surgery failure include prior radiation, severity of post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence, and previous surgeries. The meta-analysis of the extrusion rate was 9.8% and the most commonly reported adverse effects were pain and local infection. Evidence of low quality indicates that adjustable slings are effective for treating post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence, with frequency of adverse events similar to the surgical option considered gold standard (the artificial urinary sphincter implant).
RESUMO: A incontinência urinária pós-prostatectomia tem importante impacto negativo na qualidade de vida do portador. O tratamento cirúrgico inclui slings masculinos e, entre os diversos modelos, os slings ajustáveis. O objetivo deste estudo foi avaliar a efetividade e a segurança do sling ajustável no tratamento da incontinência urinária pós-prostatectomia. Trata-se de revisão sistemática de literatura. Foram pesquisadas as seguintes bases de dados eletrônicas até janeiro de 2018: PubMed®, Embase, CENTRAL e LILACS. As palavras-chaves utilizadas nas estratégias de busca foram: “prostatectomy” [Mesh], “urinary incontinence” [Mesh] e “suburethral slings” [Mesh]. Foram incluídos ensaios clínicos randomizados e estudos observacionais controlados ou não com seguimento maior que 12 meses. Apenas um estudo randomizado com alto risco de viés foi localizado e concluiu a equivalência de efetividade de slings ajustáveis e não ajustáveis. Todos os outros estudos foram série de casos com pacientes de variados níveis de intensidade da incontinência e histórico de radioterapia pélvica e cirurgias prévias. A metanálise para 0 pad em 24 horas demonstrou efetividade de 53%. Para o desfecho 0 a 1 pad em 24 horas, a metanálise resultou em efetividade de 69%. Os fatores de risco para insucesso da cirurgia incluem radiação prévia, gravidade da incontinência urinária pós-prostatectomia e cirurgias anteriores. A metanálise da taxa de extrusão foi de 9,8%, e os efeitos adversos mais relatados foram dor e infecção local. Evidências de baixa qualidade indicam que os slings ajustáveis são efetivos para o tratamento da incontinência urinária pós-prostatectomia, com frequência de eventos adversos semelhantes à opção cirúrgica considerada padrão-ouro (o implante de esfíncter urinário artificial).
Figures
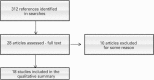



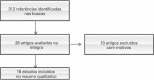



References
-
- 1. Sanda MG, Dunn RL, Michalski J, Sandler HM, Northouse L, Hembroff L, et al. Quality of life and satisfaction with outcome among prostate-cancer survivors. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(12):1250-61. - PubMed
- Sanda MG, Dunn RL, Michalski J, Sandler HM, Northouse L, Hembroff L, et al. Quality of life and satisfaction with outcome among prostate-cancer survivors. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(12):1250–1261. - PubMed
-
- 3. van der Horst C, Naumann CM, Al-Najaar A, Seif C, Stübinger SH, Jünemann KP, Braun PM. [Etiology and pathophysiology of male stress incontinence]. Urologe A. 2007;46(3):233-9. Review. German. - PubMed
- van der Horst C, Naumann CM, Al-Najaar A, Seif C, Stübinger SH, Jünemann KP, Braun PM. Etiology and pathophysiology of male stress incontinence. Urologe A. 2007;46(3):233–239. Review. German. - PubMed
-
- 4. Abrams P, Andersson KE, Birder L, Brubaker L, Cardozo L, Chapple C, Cottenden A, Davila W, de Ridder D, Dmochowski R, Drake M, Dubeau C, Fry C, Hanno P, Smith JH, Herschorn S, Hosker G, Kelleher C, Koelbl H, Khoury S, Madoff R, Milsom I, Moore K, Newman D, Nitti V, Norton C, Nygaard I, Payne C, Smith A, Staskin D, Tekgul S, Thuroff J, Tubaro A, Vodusek D, Wein A, Wyndaele JJ; Members of Committees; Fourth International Consultation on Incontinence. Fourth International Consultation on Incontinence Recommendations of the International Scientific Committee: Evaluation and treatment of urinary incontinence, pelvic organ prolapse, and fecal incontinence. Neurourol Urodyn. 2010;29(1):213-40. Review. - PubMed
- Abrams P, Andersson KE, Birder L, Brubaker L, Cardozo L, Chapple C, Cottenden A, Davila W, de Ridder D, Dmochowski R, Drake M, Dubeau C, Fry C, Hanno P, Smith JH, Herschorn S, Hosker G, Kelleher C, Koelbl H, Khoury S, Madoff R, Milsom I, Moore K, Newman D, Nitti V, Norton C, Nygaard I, Payne C, Smith A, Staskin D, Tekgul S, Thuroff J, Tubaro A, Vodusek D, Wein A, Wyndaele JJ, Members of Committees. Fourth International Consultation on Incontinence Fourth International Consultation on Incontinence Recommendations of the International Scientific Committee: Evaluation and treatment of urinary incontinence, pelvic organ prolapse, and fecal incontinence. Neurourol Urodyn. 2010;29(1):213–240. Review. - PubMed
-
- 5. Augustin H, Pummer K, Daghofer F, Habermann H, Primus G, Hubmer G. Patient self-reporting questionnaire on urological morbidity and bother after radical retropubic prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 2002;42(2):112-7. - PubMed
- Augustin H, Pummer K, Daghofer F, Habermann H, Primus G, Hubmer G. Patient self-reporting questionnaire on urological morbidity and bother after radical retropubic prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 2002;42(2):112–117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

