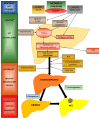
Overview of the Pathogenesis, Genetic, and Non-Invasive Clinical, Biochemical, and Scoring Methods in the Assessment of NAFLD
- PMID: 31554274
- PMCID: PMC6801903
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph16193570
Overview of the Pathogenesis, Genetic, and Non-Invasive Clinical, Biochemical, and Scoring Methods in the Assessment of NAFLD
Abstract
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most prevalent chronic liver disease worldwide. It represents a range of disorders, including simple steatosis, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and liver cirrhosis, and its prevalence continues to rise. In some cases, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) may develop. The develop;ment of non-invasive diagnostic and screening tools is needed, in order to reduce the frequency of liver biopsies. The most promising methods are those able to exclude advanced fibrosis and quantify steatosis. In this study, new perspective markers for inflammation, oxidative stress, apoptosis, and fibrogenesis; emerging scoring models for detecting hepatic steatosis and fibrosis; and new genetic, epigenetic, and multiomic studies are discussed. As isolated biochemical parameters are not specific or sensitive enough to predict the presence of NASH and fibrosis, there is a tendency to use various markers and combine them into mathematical algorithms. Several predictive models and scoring systems have been developed. Current data suggests that panels of markers (NAFLD fibrosis score, Fib-4 score, BARD score, and others) are useful diagnostic modalities to minimize the number of liver biopsies. The review unveils pathophysiological aspects related to new trends in current non-invasive biochemical, genetic, and scoring methods, and provides insight into their diagnostic accuracies and suitability in clinical practice.
Keywords: biochemical diagnostic; fibrosis; genetic diagnostic; non-invasive scoring methods; nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD); nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH); steatosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnosis of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Current Concepts.Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(38):4574-4586. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666190117102111. Curr Pharm Des. 2018. PMID: 30652642 Review.
-
Non-invasive assessment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Clinical prediction rules and blood-based biomarkers.J Hepatol. 2018 Feb;68(2):305-315. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.11.013. Epub 2017 Dec 2. J Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 29154965 Review.
-
Noninvasive evaluation of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Current evidence and practice.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Mar 21;25(11):1307-1326. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i11.1307. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30918425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current complications and challenges in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis screening and diagnosis.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;10(1):63-71. doi: 10.1586/17474124.2016.1099433. Epub 2015 Oct 15. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 26469309 Review.
-
A simple scoring system using type IV collagen 7S and aspartate aminotransferase for diagnosing nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and related fibrosis.J Gastroenterol. 2018 Jan;53(1):129-139. doi: 10.1007/s00535-017-1355-9. Epub 2017 Jun 6. J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 28589339
Cited by
-
The Effect of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Fibrosis Assessed by FIB-4 and NFS Scores-An 11.6-Year Follow-Up Study.J Clin Med. 2022 Aug 21;11(16):4910. doi: 10.3390/jcm11164910. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36013149 Free PMC article.
-
Application of PPAR Ligands and Nanoparticle Technology in Metabolic Steatohepatitis Treatment.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 16;12(8):1876. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081876. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical implications of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors for development and progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 3;11(1):2884. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-81959-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33536442 Free PMC article.
-
MAFLD/NAFLD Biopsy-Free Scoring Systems for Hepatic Steatosis, NASH, and Fibrosis Diagnosis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jan 13;8:774079. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.774079. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35096868 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Three Different Genetic Risk Scores Based on Fatty Liver Index, Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Lipidomic for a Nutrigenetic Personalized Management of NAFLD: The Fatty Liver in Obesity Study.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Jun 13;11(6):1083. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11061083. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34199237 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lonardo A., Nascimbeni F., Targher G., Bernardi M., Bonino F., Bugianesi E., Casini A., Gastaldelli A., Marchesini G., Marra F., et al. AISF position paper on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Updates and future directions. Dig. Liver Dis. 2017;49:471–483. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2017.01.147. - DOI - PubMed
-
- George E.S., Roberts S.K., Nicoll A.J., Reddy A., Paris T., Itsiopoulos C., Tierney A.C. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients attending two metropolitan hospitals in Melbourne, Australia: High risk status and low prevalence. Intern. Med. J. 2018;48:1369–1376. doi: 10.1111/imj.13973. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials