Heme-regulated eIF2α kinase in erythropoiesis and hemoglobinopathies
- PMID: 31554636
- PMCID: PMC6856985
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2019001915
Heme-regulated eIF2α kinase in erythropoiesis and hemoglobinopathies
Abstract
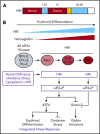
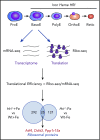
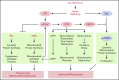
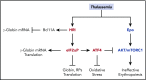
As essential components of hemoglobin, iron and heme play central roles in terminal erythropoiesis. The impairment of this process in iron/heme deficiency results in microcytic hypochromic anemia, the most prevalent anemia globally. Heme-regulated eIF2α kinase, also known as heme-regulated inhibitor (HRI), is a key heme-binding protein that senses intracellular heme concentrations to balance globin protein synthesis with the amount of heme available for hemoglobin production. HRI is activated during heme deficiency to phosphorylate eIF2α (eIF2αP), which simultaneously inhibits the translation of globin messenger RNAs (mRNAs) and selectively enhances the translation of activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) mRNA to induce stress response genes. This coordinated translational regulation is a universal hallmark across the eIF2α kinase family under various stress conditions and is termed the integrated stress response (ISR). Inhibition of general protein synthesis by HRI-eIF2αP in erythroblasts is necessary to prevent proteotoxicity and maintain protein homeostasis in the cytoplasm and mitochondria. Additionally, the HRI-eIF2αP-ATF4 pathway represses mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signaling, specifically in the erythroid lineage as a feedback mechanism of erythropoietin-stimulated erythropoiesis during iron/heme deficiency. Furthermore, ATF4 target genes are most highly activated during iron deficiency to maintain mitochondrial function and redox homeostasis, as well as to enable erythroid differentiation. Thus, heme and translation regulate erythropoiesis through 2 key signaling pathways, ISR and mTORC1, which are coordinated by HRI to circumvent ineffective erythropoiesis (IE). HRI-ISR is also activated to reduce the severity of β-thalassemia intermedia in the Hbbth1/th1 murine model. Recently, HRI has been implicated in the regulation of human fetal hemoglobin production. Therefore, HRI-ISR has emerged as a potential therapeutic target for hemoglobinopathies.
© 2019 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




References
-
- Camaschella C. Iron deficiency. Blood. 2019;133(1):30-39. - PubMed
-
- Chefalo PJ, Oh J, Rafie-Kolpin M, Kan B, Chen J-J. Heme-regulated eIF-2α kinase purifies as a hemoprotein. Eur J Biochem. 1998;258(2):820-830. - PubMed
-
- Rafie-Kolpin M, Chefalo PJ, Hussain Z, et al. . Two heme-binding domains of heme-regulated eukaryotic initiation factor-2α kinase. N-terminus and kinase insertion. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:5171-5178. - PubMed
-
- Bauer BN, Rafie-Kolpin M, Lu L, Han A, Chen JJ. Multiple autophosphorylation is essential for the formation of the active and stable homodimer of heme-regulated eIF2α kinase. Biochemistry. 2001;40(38):11543-11551. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

