FRQ-CK1 interaction determines the period of circadian rhythms in Neurospora
- PMID: 31554810
- PMCID: PMC6761100
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-12239-w
FRQ-CK1 interaction determines the period of circadian rhythms in Neurospora
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: FRQ-CK1 interaction determines the period of circadian rhythms in Neurospora.Nat Commun. 2020 Jan 14;11(1):346. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13862-3. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 31937790 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Circadian clock mechanisms have been extensively investigated but the main rate-limiting step that determines circadian period remains unclear. Formation of a stable complex between clock proteins and CK1 is a conserved feature in eukaryotic circadian mechanisms. Here we show that the FRQ-CK1 interaction, but not FRQ stability, correlates with circadian period in Neurospora circadian clock mutants. Mutations that specifically affect the FRQ-CK1 interaction lead to severe alterations in circadian period. The FRQ-CK1 interaction has two roles in the circadian negative feedback loop. First, it determines the FRQ phosphorylation profile, which regulates FRQ stability and also feeds back to either promote or reduce the interaction itself. Second, it determines the efficiency of circadian negative feedback process by mediating FRQ-dependent WC phosphorylation. Our conclusions are further supported by mathematical modeling and in silico experiments. Together, these results suggest that the FRQ-CK1 interaction is a major rate-limiting step in circadian period determination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
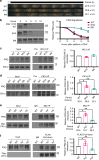

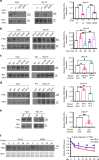
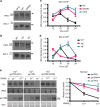
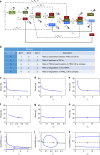
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

