R-spondin 3 promotes stem cell recovery and epithelial regeneration in the colon
- PMID: 31554819
- PMCID: PMC6761174
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-12349-5
R-spondin 3 promotes stem cell recovery and epithelial regeneration in the colon
Abstract
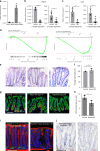
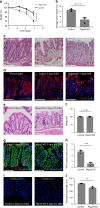
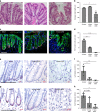
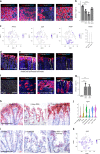
The colonic epithelial turnover is driven by crypt-base stem cells that express the R-spondin receptor Lgr5. Signals that regulate epithelial regeneration upon stem cell injury are largely unknown. Here, we explore the dynamics of Wnt signaling in the colon. We identify two populations of cells with active Wnt signaling: highly proliferative Lgr5+/Axin2+ cells, as well as secretory Lgr5-/Axin2+ cells. Upon Lgr5+ cell depletion, these cells are recruited to contribute to crypt regeneration. Chemical injury induced by DSS leads to a loss of both Lgr5+ cells and Axin2+ cells and epithelial regeneration is driven by Axin2- cells, including differentiated Krt20+ surface enterocytes. Regeneration requires stromal Rspo3, which is present at increased levels upon injury and reprograms Lgr5- but Lgr4+ differentiated cells. In contrast, depletion of stromal Rspo3 impairs crypt regeneration, even upon mild injury. We demonstrate that Rspo3 is essential for epithelial repair via induction of Wnt signaling in differentiated cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Barker N., van Es J.H., Jaks V., Kasper M., Snippert H., Toftgard R., Clevers H. Very Long-term Self-renewal of Small Intestine, Colon, and Hair Follicles from Cycling Lgr5+ve Stem Cells. Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology. 2008;73(0):351–356. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2008.72.003. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

