Relationship between preoperative high intraocular pressure and retinal nerve fibre layer thinning after glaucoma surgery
- PMID: 31554879
- PMCID: PMC6761197
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-50406-7
Relationship between preoperative high intraocular pressure and retinal nerve fibre layer thinning after glaucoma surgery
Abstract
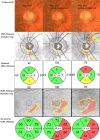
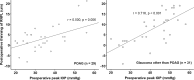
Recent reports show varying results regarding peripapillary retinal nerve fibre layer (RNFL) thickness after intraocular pressure (IOP)-lowering glaucoma surgery. We hypothesised that different levels of the preoperative IOP influence RNFL thickness. A total of 60 patients (60 eyes) with glaucoma, who underwent glaucoma surgery and had a stable postoperative mean IOP < 22 mmHg, were enrolled. The RNFL thickness was measured using spectral domain optical coherence tomography, before and at 3-6 months after surgery. The preoperative peak IOP, 37.4 ± 10.8 mmHg, decreased to a postoperative mean IOP of 14.8 ± 3.5 mmHg (p < 0.001). The average RNFL thickness was significantly reduced from 75.6 ± 17.7 μm to 70.2 ± 15.8 μm (p < 0.001). In subgroup analyses, only patients with a preoperative peak IOP ≥ median value (37 mmHg) exhibited significant RNFL thinning (9.7 ± 6.6 μm, p < 0.001) associated with a higher preoperative peak IOP (r = 0.475, p = 0.008). The RNFL thinning was evident for a few months after glaucoma surgery in patients with a higher preoperative peak IOP, although the postoperative IOP was stable.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- The effectiveness of intraocular pressure reduction in the treatment of normal-tension glaucoma. Collaborative Normal- Tension Glaucoma Study Group. Am J Ophthalmol126, 498–505 (1998). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

