Sensitization of Tumors for Attack by Virus-Specific CD8+ T-Cells Through Antibody-Mediated Delivery of Immunogenic T-Cell Epitopes
- PMID: 31555260
- PMCID: PMC6712545
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01962
Sensitization of Tumors for Attack by Virus-Specific CD8+ T-Cells Through Antibody-Mediated Delivery of Immunogenic T-Cell Epitopes
Abstract
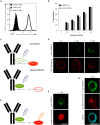
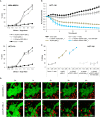
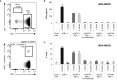
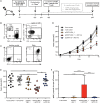
Anti-tumor immunity is limited by a number of factors including the lack of fully activated T-cells, insufficient antigenic stimulation and the immune-suppressive tumor microenvironment. We addressed these hurdles by developing a novel class of immunoconjugates, Antibody-Targeted Pathogen-derived Peptides (ATPPs), which were designed to efficiently deliver viral T-cell epitopes to tumors with the aim of redirecting virus-specific memory T-cells against the tumor. ATPPs were generated through covalent binding of mature MHC class I peptides to antibodies specific for cell surface-expressed tumor antigens that mediate immunoconjugate internalization. By means of a cleavable linker, the peptides are released in the endosomal compartment, from which they are loaded into MHC class I without the need for further processing. Pulsing of tumor cells with ATPPs was found to sensitize these for recognition by virus-specific CD8+ T-cells with much greater efficiency than exogenous loading with free peptides. Systemic injection of ATPPs into tumor-bearing mice enhanced the recruitment of virus-specific T-cells into the tumor and, when combined with immune checkpoint blockade, suppressed tumor growth. Our data thereby demonstrate the potential of ATPPs as a means of kick-starting the immune response against "cold" tumors and increasing the efficacy of checkpoint inhibitors.
Keywords: CD8+ T-cell; antibody-targeted pathogen-derived peptides (ATPP); antigen-armed antibodies; cancer immunotherapy; immune tolerance; immunogenicity; targeted therapy.
Figures



References
-
- DiJoseph JF, Dougher MM, Kalyandrug LB, Armellino DC, Boghaert ER, Hamann PR, et al. . Antitumor efficacy of a combination of CMC-544 (inotuzumab ozogamicin), a CD22-targeted cytotoxic immunoconjugate of calicheamicin, and rituximab against non-Hodgkin's B-cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. (2006) 12:242–9. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1905 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ikeda H, Hideshima T, Fulciniti M, Lutz RJ, Yasui H, Okawa Y, et al. . The monoclonal antibody nBT062 conjugated to cytotoxic Maytansinoids has selective cytotoxicity against CD138-positive multiple myeloma cells in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res. (2009) 15:4028–37. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2867 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

