Evaluation of IC50 levels immediately after treatment with anticancer reagents using a real-time cell monitoring device
- PMID: 31555392
- PMCID: PMC6755379
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.7876
Evaluation of IC50 levels immediately after treatment with anticancer reagents using a real-time cell monitoring device
Abstract
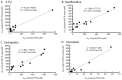
A real-time cell-monitoring analysis (RTCA) system was previously developed based on the change in impedance when cells attach and spread in a culture dish coated with a gold microelectrode array. However, the potential applications of this system have not yet been fully demonstrated. The purpose of this study was to test the utility of the RTCA system to determine the cytotoxicity of four anticancer agents in carcinoma cells. The results were compared with those of the conventional WST-8 assay at the endpoint to determine the potential of the RTCA system as a new real-time assay method to evaluate cytotoxicity. iCELLigence was used as the RTCA system in this study. Suspensions of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cell lines were seeded (2×104 cells/well) onto the E-plate (the culture plate of the iCELLigence system). After 24 h of culture, anticancer agents were added to each well, and changes in electrical impedance (cell index, CI) were recorded for another 72 h of culture. Cell proliferation was detected in real-time by the RTCA device in an automated, high throughput manner. Then, the IC50 profiles of the four anticancer agents were calculated based on the real-time cell index values. The results indicated that the RTCA system was useful in evaluating cytotoxic reactions immediately after the addition of the anticancer agents as it was able to record the data in real-time. Furthermore, the IC50 levels measured by the real-time assay were lower than those measured by the endpoint assay. Thus, RTCA systems can be used to evaluate chemotherapeutic agents in cancer cells as well as their side effects in normal cells.
Keywords: IC50; RTCA system; anticancer reagent; cytotoxicity; squamous cell carcinoma.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Real-time cell-microelectronic sensing of nanoparticle-induced cytotoxic effects.Anal Chim Acta. 2013 Jul 30;789:83-90. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2013.06.002. Epub 2013 Jun 18. Anal Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23856233
-
iCELLigence real-time cell analysis system for examining the cytotoxicity of drugs to cancer cell lines.Exp Ther Med. 2017 Sep;14(3):1866-1870. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4781. Epub 2017 Jul 11. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 28962095 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of cytotoxicity assay by real-time, impedance-based cell analysis.Biomed Microdevices. 2013 Dec;15(6):985-95. doi: 10.1007/s10544-013-9790-8. Biomed Microdevices. 2013. PMID: 23887614
-
Real-time cell analysis system in cytotoxicity applications: Usefulness and comparison with tetrazolium salt assays.Toxicol Rep. 2020 Feb 7;7:335-344. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2020.02.002. eCollection 2020. Toxicol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32090021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Real-Time Cell Electronic Analysis System in Modern Pharmaceutical Evaluation and Analysis.Molecules. 2018 Dec 11;23(12):3280. doi: 10.3390/molecules23123280. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30544947 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of Cell Viability in Drug Therapy: IC50 and Other New Time-Independent Indices for Evaluating Chemotherapy Efficacy.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Feb 13;17(2):247. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17020247. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40006615 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Peptaibol's Profile, Antifungal, and Antitumor Activity of Emericellipsin A of Emericellopsis Species from Soda and Saline Soils.Molecules. 2022 Mar 7;27(5):1736. doi: 10.3390/molecules27051736. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35268835 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive Properties and In Vitro Digestive Release of Cannabidiol (CBD) from Tailored Composites Based on Carbon Materials.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Aug 27;16(9):1132. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16091132. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39339170 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced oral delivery of hesperidin-loaded sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin/chitosan nanoparticles for augmenting its hypoglycemic activity: in vitro-in vivo assessment study.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024 Apr;14(4):895-917. doi: 10.1007/s13346-023-01440-6. Epub 2023 Oct 16. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 37843733 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of silver-nanoparticles and whey-encapsulated particles from olive leaf water extracts: Characteristics and biological activity.PLoS One. 2023 Dec 18;18(12):e0296032. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0296032. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 38109310 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
