A Reappraisal of Thymosin Alpha1 in Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 31555601
- PMCID: PMC6742685
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00873
A Reappraisal of Thymosin Alpha1 in Cancer Therapy
Abstract
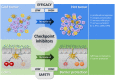
Thymosin alpha1 (Tα1), an endogenous peptide first isolated from the thymic tissue in the mid-sixties, has gained considerable attention for its immunostimulatory activity that led to its application to diverse pathological conditions, including cancer. Studies in animal models and human patients have shown promising results in different types of malignancies, especially when Tα1 was used in combination with other chemo- and immune therapies. For this reason, the advancements in our knowledge on the adjuvant role of Tα1 have moved in parallel with the development of novel cancer therapies in a way that Tα1 was integrated to changing paradigms and protocols, and tested for increased efficacy and safety. Cancer immunotherapy has recently experienced a tremendous boost following the development and clinical application of immune checkpoint inhibitors. By unleashing the full potential of the adaptive immune response, checkpoint inhibitors were expected to be very effective against tumors, but it soon became clear that a widespread and successful application was not straightforward and shortcomings in efficacy and safety clearly emerged. This scenario led to the development of novel concepts in immunotherapy and the design of combination protocols to overcome these limitations, thus opening up novel opportunities for Tα1 application. Herein, we summarize in a historical perspective the use of Tα1 in cancer, with particular reference to melanoma, hepatocellular carcinoma and lung cancer. We will discuss the current limitations of checkpoint inhibitors in clinical practice and the mechanisms at the basis of a potential application of Tα1 in combination protocols.
Keywords: checkpoint inhibitors; colitis; dendritic cells; immunotherapy; thymosin alpha1.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

