Mutation in LDL receptor: Alu-Alu recombination deletes exons encoding transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains
- PMID: 3155573
- PMCID: PMC4449727
- DOI: 10.1126/science.3155573
Mutation in LDL receptor: Alu-Alu recombination deletes exons encoding transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains
Abstract
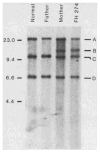
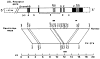
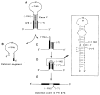
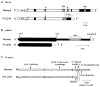
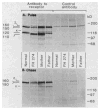
The molecular size of the plasma LDL (low density lipoprotein) receptor synthesized by cultured fibroblasts from a patient with the internalization-defective form of familial hypercholesterolemia (FH 274) was smaller by 10,000 daltons than the size of the normal LDL receptor. The segment of the gene encoding the truncated portion of the FH 274 receptor was cloned into bacteriophage lambda. Comparison of the nucleotide sequences of the normal and FH 274 genes revealed a 5-kilobase deletion, which eliminated the exons encoding the membrane-spanning region and the carboxyl terminal cytoplasmic domain of the receptor. The deletion appeared to be caused by a novel intrastrand recombination between two repetitive sequences of the Alu family that were oriented in opposite directions. The truncated receptors lack membrane-spanning regions and cytoplasmic domains; they are largely secreted into the culture medium, but a small fraction remains adherent to the cell surface. The surface-adherent receptors bind LDL, but they are unable to cluster in coated pits, thus explaining the internalization-defective phenotype.
Figures
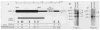



References
-
- Goldstein JL, Brown MS. In: The Metabolic Basis of Inherited Disease. 5. Stanbury JB, Wyngaarden JB, Fredrickson DS, Goldstein JL, Brown MS, editors. chap 33. McGraw-Hill; New York: 1984. pp. 672–712.
-
- Goldstein JL, Anderson RGW, Brown MS. Nature (London) 1979;279:679. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

