Molecular Characterization of Lipoaspirates Used in Regenerative Head and Neck Surgery
- PMID: 31556908
- PMCID: PMC6764019
- DOI: 10.1001/jamafacial.2019.0851
Molecular Characterization of Lipoaspirates Used in Regenerative Head and Neck Surgery
Abstract
Importance: Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ASCs) have been used commonly in regenerative medicine and increasingly for head and neck surgical procedures. Lipoaspiration with centrifugation is purported to be a mild method for the extraction of ASCs used for autologous transplants to restore tissue defects or induce wound healing. The content of ASCs, their paracrine potential, and cellular potential in wound healing have not been explored for this method to our knowledge.
Objective: To evaluate the characteristics of lipoaspirates used in reconstructive head and neck surgical procedures with respect to wound healing.
Design, setting, and participants: This case series study included 15 patients who received autologous fat injections in the head and neck during surgical procedures at a tertiary referral center. The study was performed from October 2017 to November 2018, and data were analyzed from October 2017 to February 2019.
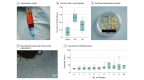
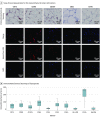
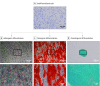
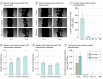
Main outcomes and measures: Excessive material of lipoaspirates from subcutaneous abdominal fatty tissue was examined. Cellular composition was analyzed using immunohistochemistry (IHC) and flow cytometry, and functionality was assessed through adipose, osteous, and chondral differentiation in vitro. Supernatants were tested for paracrine ASC functions in fibroblast wound-healing assays. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay measurement of tumor necrosis factor (TNF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), stromal-derived factor 1α (SDF-1α), and transforming growth factor β3 (TGF-β3) was performed.
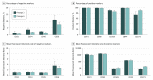
Results: Among the 15 study patients (8 [53.3%] male; mean [SD] age at the time of surgery, 63.0 [2.8] years), the stromal vascular fraction (mean [SE], 53.3% [4.2%]) represented the largest fraction within the native lipoaspirates. The cultivated cells were positive for CD73 (mean [SE], 99.90% [0.07%]), CD90 (99.40% [0.32%]), and CD105 (88.54% [2.74%]); negative for CD34 (2.70% [0.45%]) and CD45 (1.74% [0.28%]) in flow cytometry; and negative for CD14 (10.56 [2.81] per 300 IHC score) and HLA-DR (6.89 [2.97] per 300 IHC score) in IHC staining; they differentiated into osteoblasts, adipocytes, and chondrocytes. The cultivated cells showed high expression of CD44 (mean [SE], 99.78% [0.08%]) and CD273 (82.56% [5.83%]). The supernatants were negative for TNF (not detectable) and SDF-1α (not detectable) and were positive for VEGF (mean [SE], 526.74 [149.84] pg/mL for explant supernatants; 528.26 [131.79] pg/106 per day for cell culture supernatants) and TGF-β3 (mean [SE], 22.79 [3.49] pg/mL for explant supernatants; 7.97 [3.15] pg/106 per day for cell culture supernatants). Compared with control (25% or 50% mesenchymal stem cell medium), fibroblasts treated with ASC supernatant healed the scratch-induced wound faster (mean [SE]: control, 1.000 [0.160]; explant supernatant, 1.369 [0.070]; and passage 6 supernatant, 1.492 [0.094]).
Conclusions and relevance: The cells fulfilled the international accepted criteria for mesenchymal stem cells. The lipoaspirates contained ASCs that had the potential to multidifferentiate with proliferative and immune-modulating properties. The cytokine profile of the isolated ASCs had wound healing-promoting features. Lipoaspirates may have a regenerative potential and an application in head and neck surgery.
Level of evidence: NA.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Bashir MM, Sohail M, Bashir A, et al. Outcome of conventional adipose tissue grafting for contour deformities of face and role of ex vivo expanded adipose tissue-derived stem cells in treatment of such deformities. J Craniofac Surg. 2018;29(5):1143-1147. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000004367 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
