Positron Emission Tomography-Guided Photodynamic Therapy with Biodegradable Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy
- PMID: 31556987
- PMCID: PMC6832743
- DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.9b06691
Positron Emission Tomography-Guided Photodynamic Therapy with Biodegradable Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy
Abstract
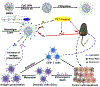
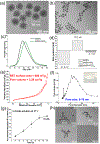
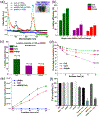
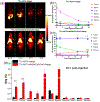
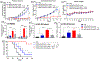
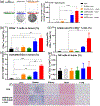
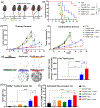
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is an effective, noninvasive therapeutic modality against local tumors that are accessible to the source of light. However, it remains challenging to apply PDT for the treatment of disseminated, metastatic cancer. On the other hand, cancer immunotherapy offers a promising approach for generating systemic antitumor immune responses against disseminated cancer. Here we report a multifunctional nanomaterial system for the combination of PDT and personalized cancer immunotherapy and demonstrate their potency against local as well as disseminated tumors. Specifically, we have synthesized uniform and biodegradable mesoporous silica nanoparticles (bMSN) with an average size of ∼80 nm and large pore size of 5-10 nm for theranostic positron emission tomography (PET)-guided PDT and neoantigen-based cancer vaccination. Multiple neoantigen peptides, CpG oligodeoxynucleotide adjuvant, and photosensitizer chlorin e6 were coloaded into a bMSN nanoplatform, and PET imaging revealed effective accumulation of bMSN in tumors (up to 9.0% ID/g) after intravenous administration. Subsequent PDT with laser irradiation recruited dendritic cells to PDT-treated tumor sites and elicited neoantigen-specific, tumor-infiltrating cytotoxic T-cell lymphocytes. Using multiple murine models of bilateral tumors, we demonstrate strong antitumor efficacy of PDT-immunotherapy against locally treated tumors as well as distant, untreated tumors. Our findings suggest that the bMSN is a promising platform for combining imaging and PDT-enhanced personalized immunotherapy for the treatment of advanced cancer.
Keywords: cancer immunotherapy; mesoporous silica nanoparticles; neoantigen; photodynamic therapy; positron emission tomography; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Lucky SS; Soo KC; Zhang Y Nanoparticles in Photodynamic Therapy. Chem. Rev 2015, 115, 1990–2042. - PubMed
-
- Wang C; Tao H; Cheng L; Liu Z Near-Infrared Light Induced In Vivo Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer Based on Upconversion Nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 6145–6154. - PubMed
-
- Yuan Y; Zhang CJ; Gao M; Zhang R; Tang BZ; Liu B Specific Light-Up Bioprobe with Aggregation-Induced Emission and Activatable Photoactivity for the Targeted and Image-Guided Photodynamic Ablation of Cancer Cells. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed 2015, 54, 1780–1786. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

