Allele-specific RNA interference prevents neuropathy in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2D mouse models
- PMID: 31557132
- PMCID: PMC6877339
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI130600
Allele-specific RNA interference prevents neuropathy in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2D mouse models
Abstract
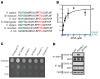
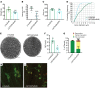
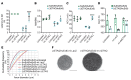
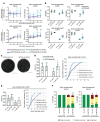
Gene therapy approaches are being deployed to treat recessive genetic disorders by restoring the expression of mutated genes. However, the feasibility of these approaches for dominantly inherited diseases - where treatment may require reduction in the expression of a toxic mutant protein resulting from a gain-of-function allele - is unclear. Here we show the efficacy of allele-specific RNAi as a potential therapy for Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2D (CMT2D), caused by dominant mutations in glycyl-tRNA synthetase (GARS). A de novo mutation in GARS was identified in a patient with a severe peripheral neuropathy, and a mouse model precisely recreating the mutation was produced. These mice developed a neuropathy by 3-4 weeks of age, validating the pathogenicity of the mutation. RNAi sequences targeting mutant GARS mRNA, but not wild-type, were optimized and then packaged into AAV9 for in vivo delivery. This almost completely prevented the neuropathy in mice treated at birth. Delaying treatment until after disease onset showed modest benefit, though this effect decreased the longer treatment was delayed. These outcomes were reproduced in a second mouse model of CMT2D using a vector specifically targeting that allele. The effects were dose dependent, and persisted for at least 1 year. Our findings demonstrate the feasibility of AAV9-mediated allele-specific knockdown and provide proof of concept for gene therapy approaches for dominant neuromuscular diseases.
Keywords: Gene therapy; Genetic diseases; Genetics; Neuromuscular disease; Neuroscience.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

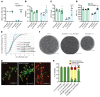
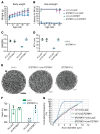
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- U54 OD020351/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS054154/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR062123/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG006542/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007863/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM094231/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F30 NS092238/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS054154/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI139202/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS101166/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 NS054154/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM118647/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F31 NS100328/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007315/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM134931/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA034196/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD060848/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- F31 NS108510/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 NS105078/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS105116/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F31 NS098540/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AR070604/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007544/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS058529/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 NS107751/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

