Improving Communication in Heart Failure Patient Care
- PMID: 31558252
- PMCID: PMC7000126
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.07.058
Improving Communication in Heart Failure Patient Care
Abstract
Background: Although implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) reduce sudden death, these patients die of heart failure (HF) or other diseases. To prevent shocks at the end of life, clinicians should discuss deactivating the defibrillation function.
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to determine if a clinician-centered teaching intervention and automatic reminders increased ICD deactivation discussions and increased device deactivation.
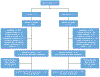
Methods: In this 6-center, single-blinded, cluster-randomized, controlled trial, primary outcomes were proportion of patients: 1) having ICD deactivation discussions; and 2) having the shocking function deactivated. Secondary outcomes included goals of care conversations and advance directive completion.
Results: A total of 525 subjects were included with advanced HF who had an ICD: 301 intervention and 224 control. At baseline, 52% (n = 272) were not candidates for advanced therapies (i.e., cardiac transplant or mechanical circulatory support). There were no differences in discussions (41 [14%] vs. 26 [12%]) or deactivation (33 [11%] vs. 26 [12%]). In pre-specified subgroup analyses of patients who were not candidates for advanced therapies, the intervention increased deactivation discussions (32 [25%] vs. 16 [11%]; odds ratio: 2.90; p = 0.003). Overall, 99 patients died; there were no differences in conversations or deactivations among decedents.
Secondary outcomes: Among all participants, there was an increase in goals of care conversations (47% intervention vs. 38% control; odds ratio: 1.53; p = 0.04). There were no differences in completion of advance directives.
Conclusions: The intervention increased conversations about ICD deactivation and goals of care. HF clinicians were able to apply new communication techniques based on patients' severity of illness. (An Intervention to Improve Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Deactivation Conversations [WISDOM]; NCT01459744).
Keywords: communication; heart failure; implantable defibrillator; palliative care.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
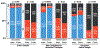
Comment in
-
Training, Triggers, and a Team for the Right Discussions.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 Oct 1;74(13):1693-1696. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.07.059. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31558253 No abstract available.
References
-
- Moss AJ, Zareba W, Hall WJ et al. Prophylactic Implantation of a Defibrillator in Patients with Myocardial Infarction and Reduced Ejection Fraction. N Engl J Med 2002;346:877–883. - PubMed
-
- Bardy GH, Lee KL, Mark DB et al. Amiodarone or an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator for congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med 2005;352:225–37. - PubMed
-
- Glikson M, Friedman PA. The Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator. Lancet 2001;357:1107–1117. - PubMed
-
- Eckert M, Jones T. How Does an Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD) Affect the Lives of Patients and Their Families? Int J Nurs Pract 2002;8:152–157. - PubMed
-
- Lampert R, Hayes DL, Annas GJ et al. HRS Expert Consensus Statement on the Management of Cardiovascular Implantable Electronic Devices (CIEDs) in patients nearing end of life or requesting withdrawal of therapy. Heart Rhythm 2010;7:1008–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

