Retinoid X receptor gamma (RXRG) is an independent prognostic biomarker in ER-positive invasive breast cancer
- PMID: 31558802
- PMCID: PMC6889395
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-019-0589-0
Retinoid X receptor gamma (RXRG) is an independent prognostic biomarker in ER-positive invasive breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Retinoid X Receptor Gamma (RXRG) is a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily and plays a role in tumour suppression. This study aims to explore the prognostic significance of RXRG in breast cancer.
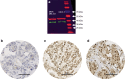
Methods: Primary breast cancer tissue microarrays (n = 923) were immuno-stained for RXRG protein and correlated with clinicopathological features, and patient outcome.
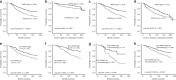
Results: Nuclear RXRG expression was significantly associated with smaller tumour size (p = 0.036), lower grade (p < 0.001), lobular histology (p = 0.016), lower Nottingham Prognostic Index (p = 0.04) and longer breast cancer-specific survival (p < 0.001), and longer time to distant metastasis (p = 0.002). RXRG expression showed positive association with oestrogen receptor (ER)-related biomarkers: GATA3, FOXA1, STAT3 and MED7 (all p < 0.001) and a negative correlation with the Ki67 proliferation marker. Multivariate analysis demonstrated RXRG protein as an independent predictor of longer breast cancer-specific survival and distant metastasis-free survival. In the external validation cohorts, RXRG expression was associated with improved patients' outcome (p = 0.025). In ER-positive tumours, high expression of RXRG was associated with better patient outcome regardless of adjuvant systemic therapy. ER signalling pathway was the top predicted master regulator of RXRG protein expression (p = 0.005).
Conclusion: This study provides evidence for the prognostic value of RXRG in breast cancer particularly the ER-positive tumours.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer. 2015;136:E359–E386. - PubMed
-
- Doan TB, Graham JD, Clarke CL. Emerging functional roles of nuclear receptors in breast cancer. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2017;58:R169–R190. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

